Ship to: 43215 Update
- Plants
- Fruit Trees
- Fruit Trees
- Nut Trees
Plants Filter
Current Filters
Mature Height
Sunlight
Plant Type
Nut Trees
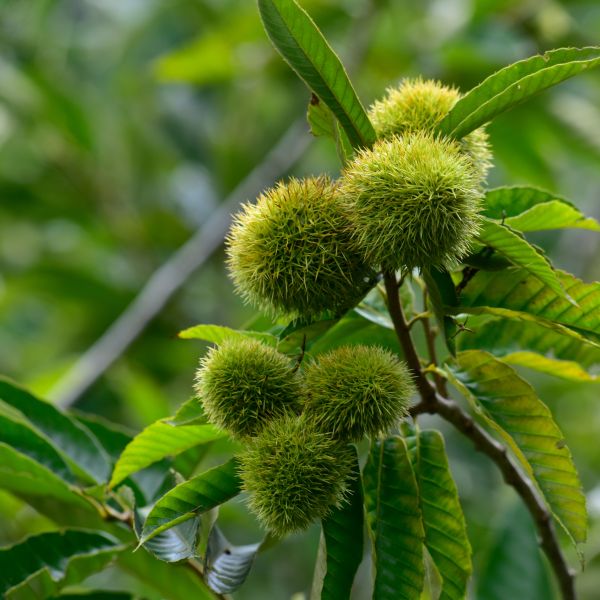

Chinese Chestnut
Starting at $77
30% Off
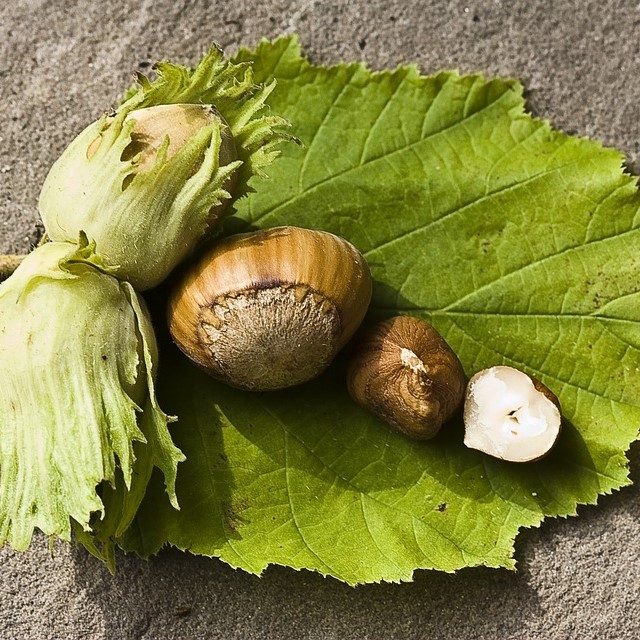

Hazelnut
Starting at $115
30% Off
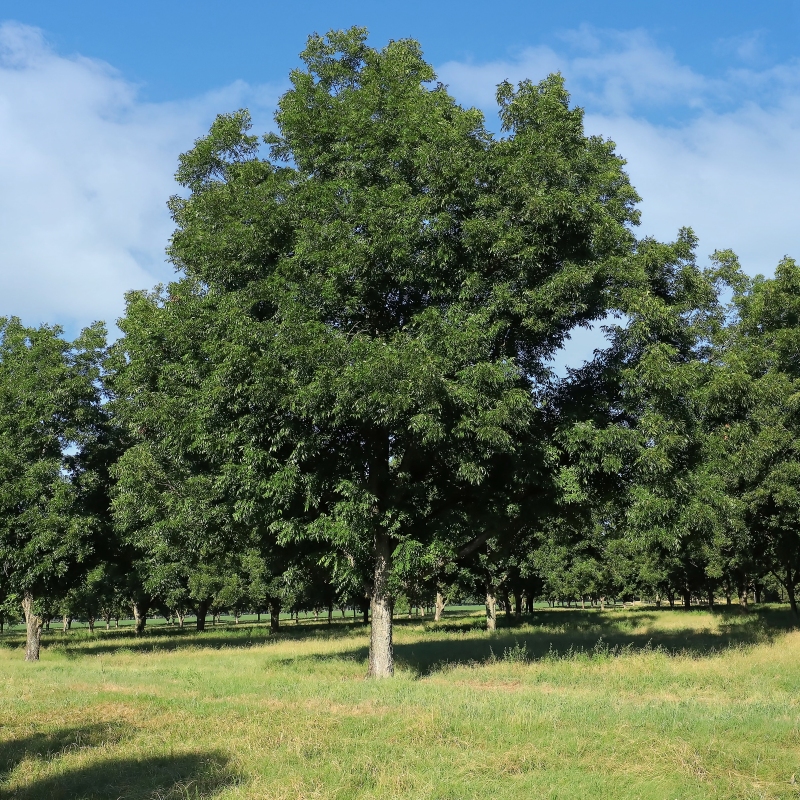

Native Pecan Tree
Starting at $90
30% Off
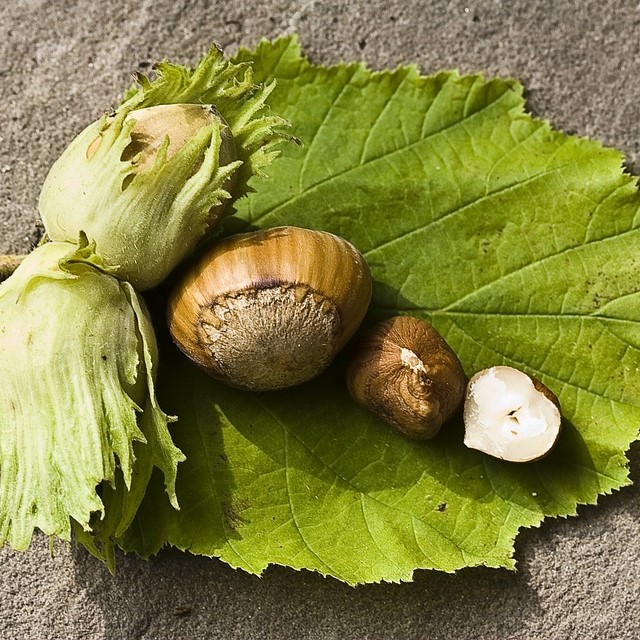

American Hazelnut Filbert Tree
Out of Stock
30% Off
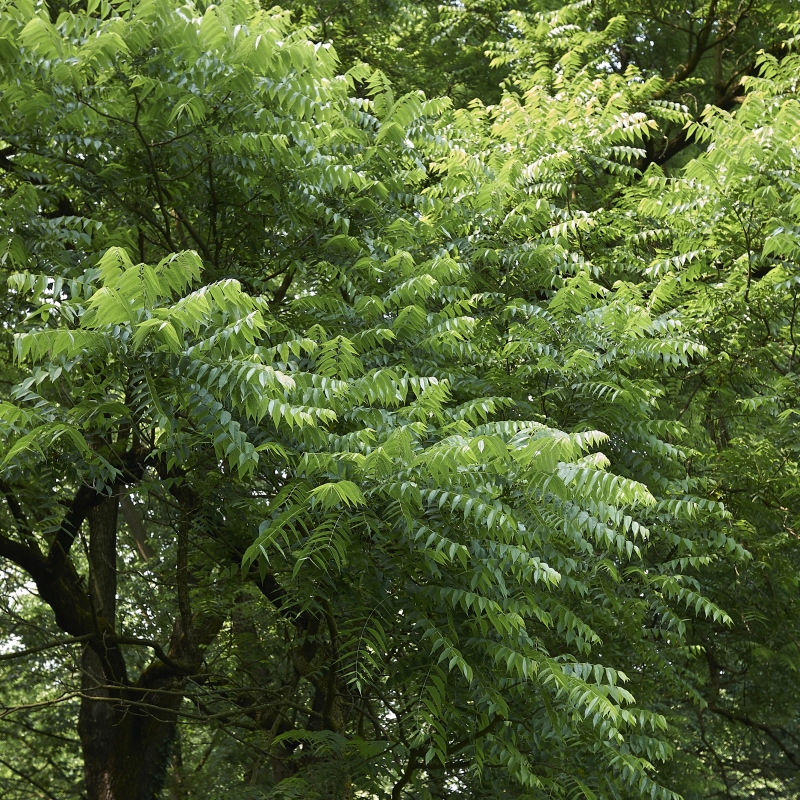

Black Walnut Tree
Out of Stock
30% Off
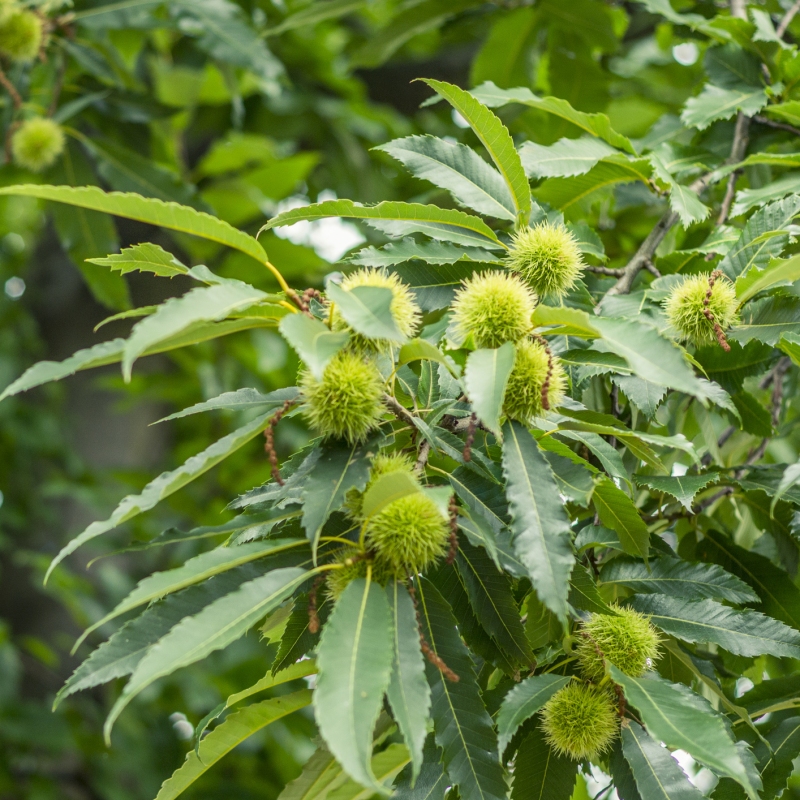

Chinese Chestnut Tree
Out of Stock
30% Off
Nut Trees
Nut trees are a group of deciduous or evergreen trees that produce edible nuts. These trees belong to various genera and families, and they are valued for their nutritious and flavorful nuts, which serve as important food sources for both humans and wildlife. Nut trees can be found in different parts of the world, and they play a vital role in various cultures, cuisines, and ecosystems.

Common Nut Tree Varieties:
- Walnut (Juglans spp.): Walnuts are large, single-seeded nuts that come from trees of the Juglans genus. Common species include the English walnut (Juglans regia) and the black walnut (Juglans nigra).
- Almond (Prunus dulcis): Almonds are small, single-seeded nuts produced by the almond tree. They are widely cultivated for their culinary uses and nutritional value.
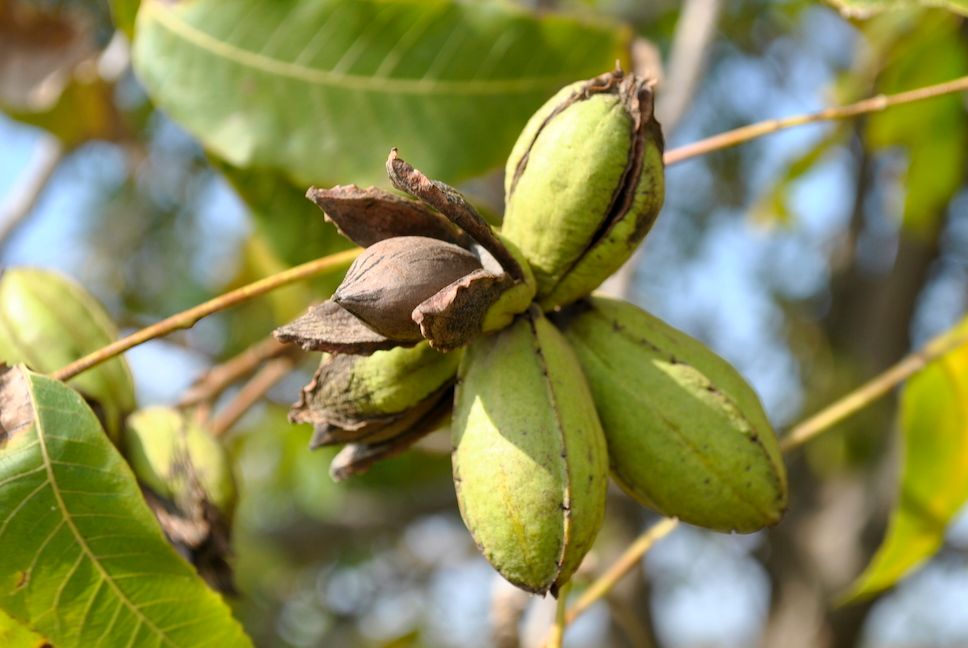
- Pecan (Carya illinoinensis): Pecans are native to North America and are known for their rich, buttery flavor. The pecan tree belongs to the Carya genus.
- Hazelnut (Corylus spp.): Hazelnuts, also known as filberts, are small, round nuts produced by trees of the Corylus genus. Common species include the European hazelnut (Corylus avellana) and the American hazelnut (Corylus americana).
- Chestnut (Castanea spp.): Chestnuts are sweet and starchy nuts produced by trees of the Castanea genus. They are often roasted and used in various culinary dishes.

Care Tips:
- Location: Plant nut trees in a location with full sun to ensure optimal growth and nut production.
- Soil: Nut trees prefer well-draining, fertile soil with good organic matter. Soil pH requirements may vary depending on the tree species.
- Watering: Keep young nut trees well-watered to establish their root systems. Once established, they have moderate water needs.
- Fertilization: Fertilize nut trees with a balanced fertilizer to promote healthy growth and nut development.
- Pruning: Regular pruning may be necessary to remove dead or diseased wood and shape the tree for better air circulation and light penetration. Some nut trees may also require specific pruning techniques to encourage better nut production.

Uses:
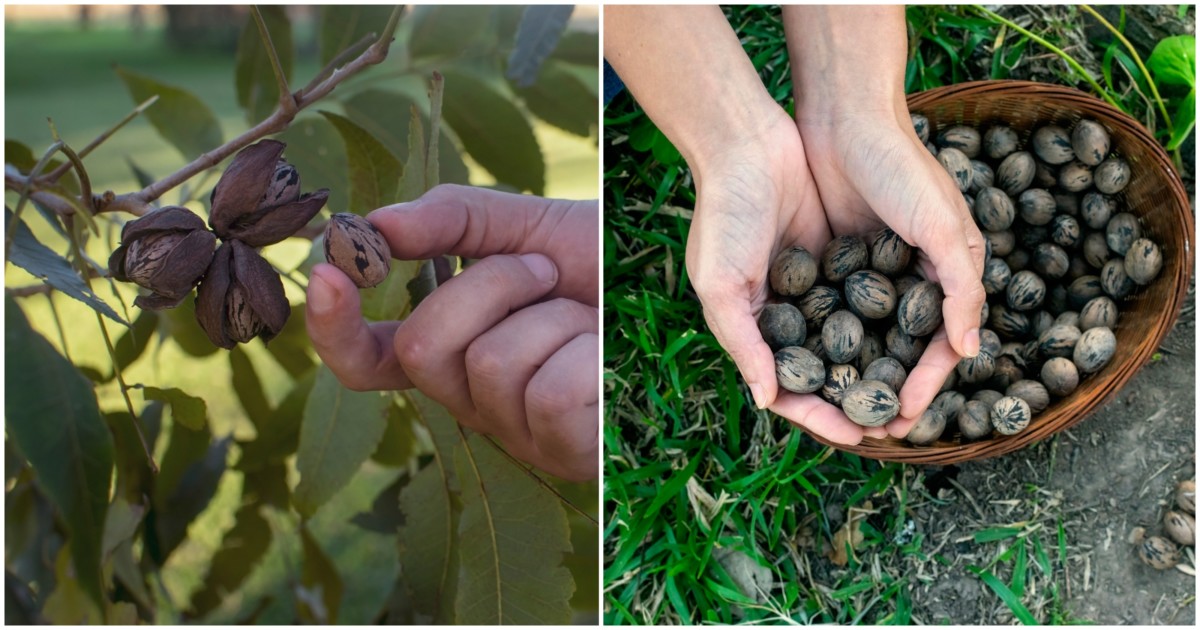
- Edible Nuts: The primary use of nut trees is for the production of edible nuts, which are enjoyed fresh, roasted, or used in various culinary dishes and desserts.
- Cooking and Baking: Nuts add flavor, texture, and nutrition to a wide range of dishes, including salads, cakes, cookies, and savory dishes.
- Nut Oils: Some nut trees, like walnut and almond trees, are cultivated for their oil-rich nuts, which are used for cooking and in various products.
- Wildlife Food Source: Nut trees play a crucial role in supporting wildlife populations, providing valuable food sources for birds, squirrels, and other animals.
Nut trees are valuable additions to both orchards and home gardens, offering not only nutritious nuts but also ornamental beauty. Depending on the tree species, nut trees may have specific care requirements, but with proper attention and care, they can thrive and provide a bounty of delicious and nutritious nuts for years to come.
Item has been added to your cart.

