Ship to: 43215 Update
- Plants
- Perennials
- Perennials
- Lavender
Plants Filter
Current Filters
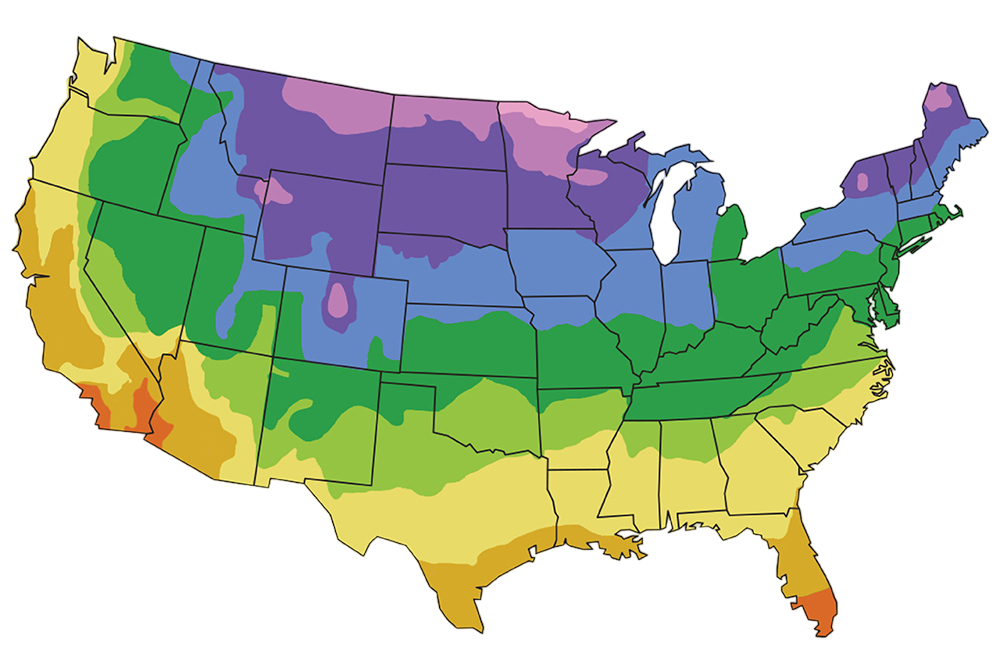
Mature Height
Sunlight
Plant Type
Lavender
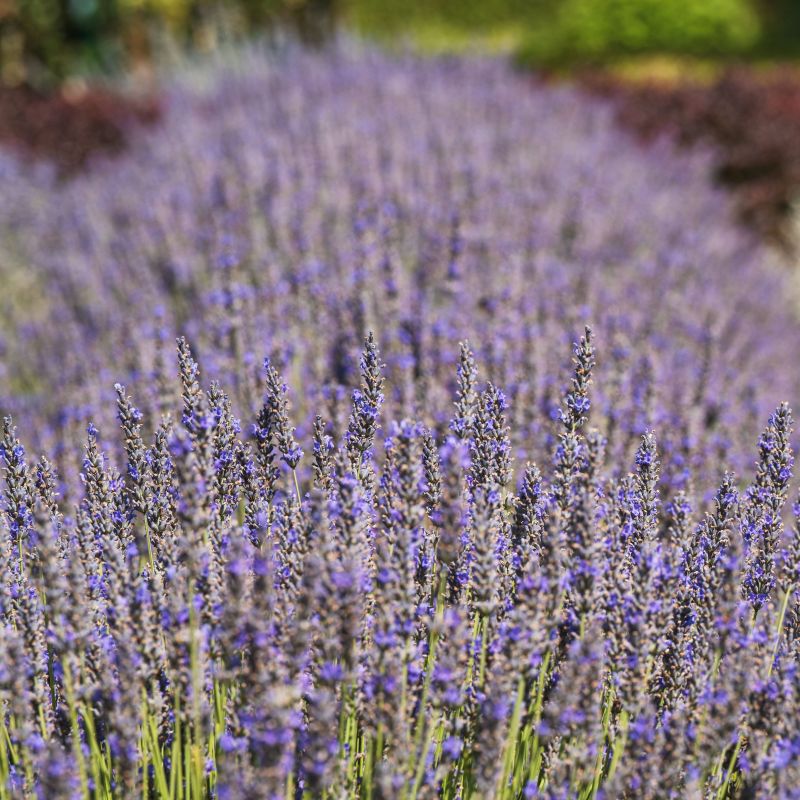

English Munstead Lavender
Starting at $76
30% Off
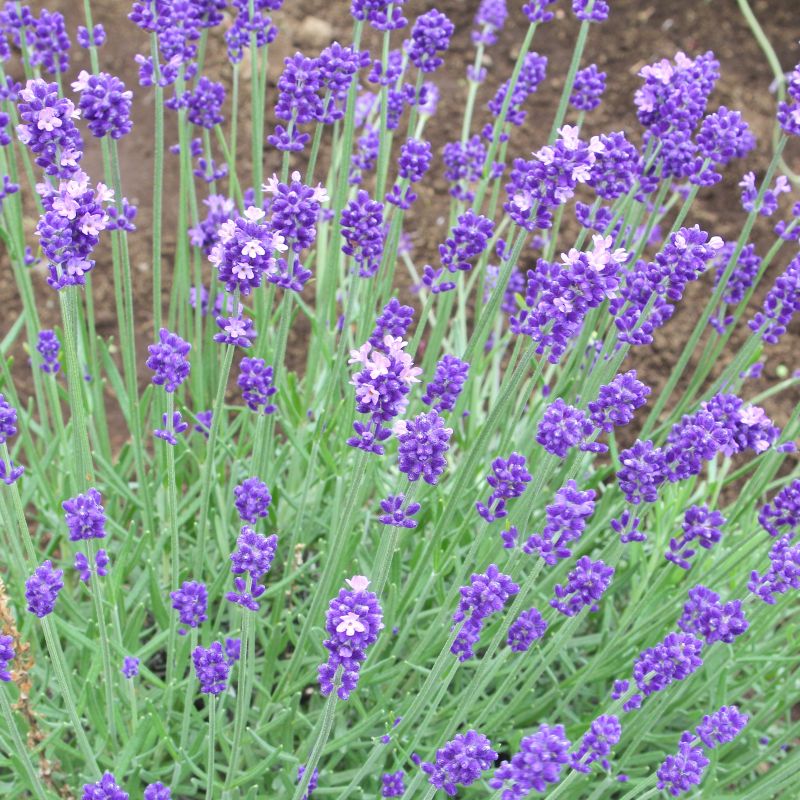

Hidcote Lavender
Starting at $49
30% Off
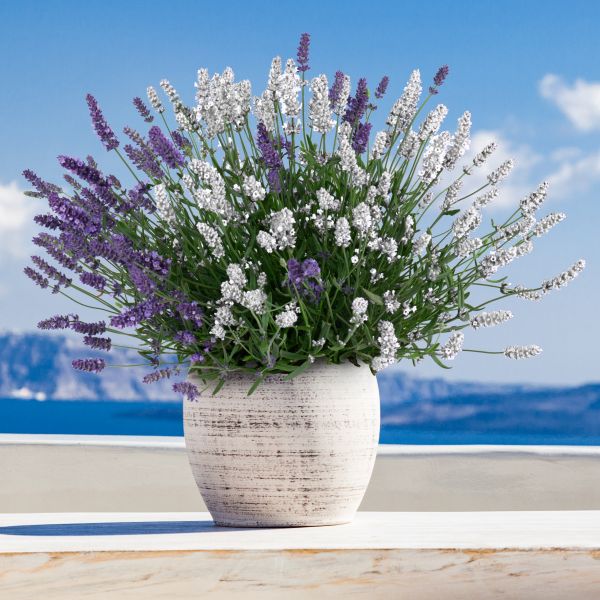

Lavandula Big Time Duet Lavender
Starting at $46
30% Off

Lavandula Big Time Duet Lavender - 3pc
Starting at $65
30% Off
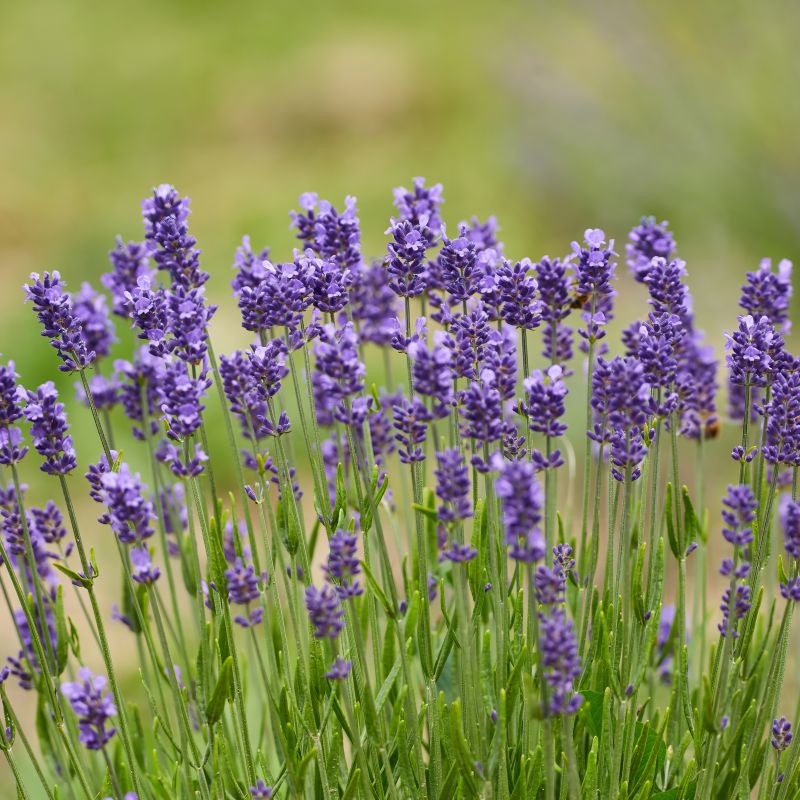

Lavandula, Super Blue Lavender
Starting at $43
30% Off
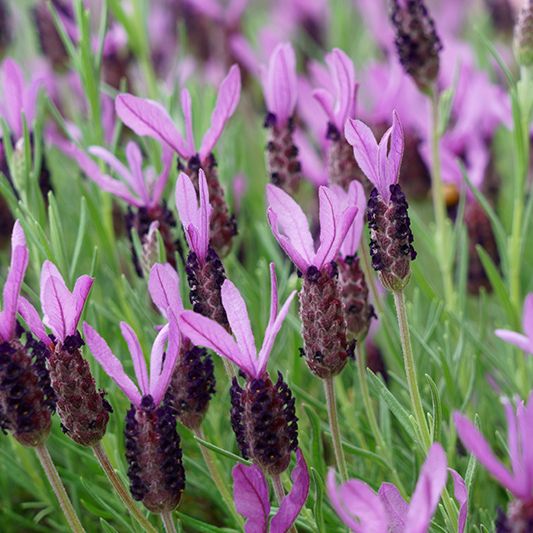

Phenomenal French Lavender
Starting at $36
30% Off
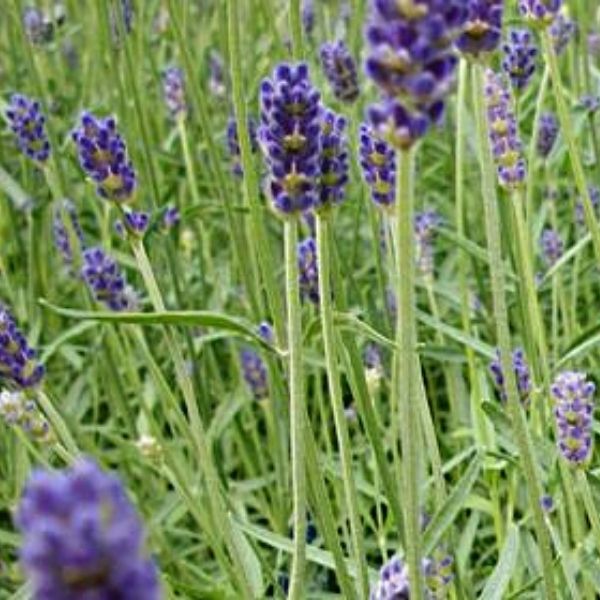

Provence Lavender
Starting at $36
30% Off
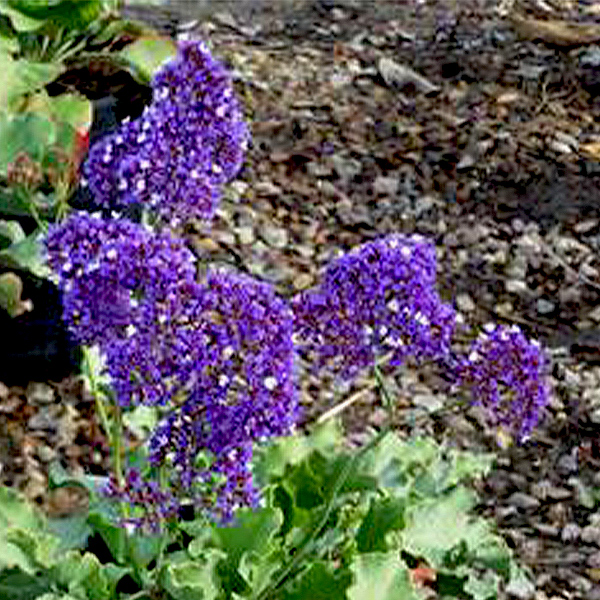

Sea Lavender
Starting at $49
30% Off

Sensational! Lavender
Starting at $37
30% Off

Avignon Early Blue Lavender
Out of Stock
30% Off

Grosso Lavender
Out of Stock
30% Off

Imperial Gem English Lavender
Out of Stock
30% Off

Lavandula Annet
Out of Stock
30% Off

Lavandula Collection
Out of Stock
30% Off

Lavandula, Layla™ Presto Blue Lavender
Out of Stock
30% Off

Silver Mist English Lavender
Out of Stock
30% Off
Lavender
Lavender, scientifically known as Lavandula, is a genus of aromatic flowering plants in the Lamiaceae (mint) family. Native to the Mediterranean region, lavender is cherished for its delightful fragrance, beautiful flowers, and various culinary, medicinal, and ornamental uses. Lavender plants are small to medium-sized, evergreen shrubs with slender, silvery-green leaves and spikes of tiny, fragrant flowers. The flowers are tubular in shape and typically come in shades of purple, lavender, blue, and sometimes pink or white, depending on the species and variety.

Common Species and Cultivars: There are many species and cultivars of lavender, each with its unique characteristics and uses. Some popular ones include:
- Lavandula angustifolia (English Lavender): Known for its sweet fragrance and compact growth habit, often used in culinary applications and essential oil production.
- Lavandula x intermedia (Lavandin): A hybrid between English lavender and spike lavender, often cultivated for its higher oil content and larger size.
- Lavandula stoechas (Spanish Lavender): Recognized by its distinctive "rabbit ears" bracts at the top of the flower spikes.
- Lavandula dentata (French Lavender): Has toothed leaves and produces aromatic lavender flowers with serrated petals.

Care Tips:
- Sunlight: Lavender thrives in full sun and requires at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight per day for optimal growth and flowering.
- Soil: Well-draining soil is crucial for lavender. It prefers sandy or loamy soil with good drainage.
- Watering: Lavender is drought-tolerant once established. Water young plants regularly until they establish their root systems, but avoid overwatering.
- Pruning: Prune lavender plants after flowering to remove spent flower spikes and promote bushier growth.
- Fertilization: Lavender doesn't require heavy fertilization. A light application of balanced fertilizer in the spring can support healthy growth.
- Overwintering: In colder climates, protect lavender plants from harsh winter conditions by applying a layer of mulch around the base.

Uses:
- Aromatic Garden: Lavender is widely used in aromatic gardens for its delightful fragrance, which attracts bees, butterflies, and other pollinators.
- Herb Gardens: Lavender is a popular herb used in culinary applications, such as flavoring desserts, teas, and savory dishes.
- Medicinal Uses: Lavender has a long history of medicinal use for its calming properties and potential benefits for relaxation and stress relief.
- Crafts and Potpourri: Lavender flowers are commonly used in crafting potpourri, sachets, and homemade scented products.
- Ornamental Landscapes: Lavender is frequently used in ornamental landscapes as a low-maintenance, drought-tolerant plant that provides visual interest and texture.
Lavender is adored for its versatility, captivating scent, and multitude of applications, making it one of the most beloved and widely used plants in gardens around the world. Whether grown for its culinary uses, ornamental beauty, or aromatherapy benefits, lavender brings a touch of elegance and tranquility to any garden or landscape.
Whether you are seeking relaxation, aromatherapy, natural beauty products, or simply love the calming scent of lavender, this category has a range of amazing products to fulfill your needs. Embrace the serenity and beauty of lavender with these carefully curated items.
Item has been added to your cart.

