Ship to: Update
Plants Filter
Current Filters
Mature Height
Sunlight
Plant Type
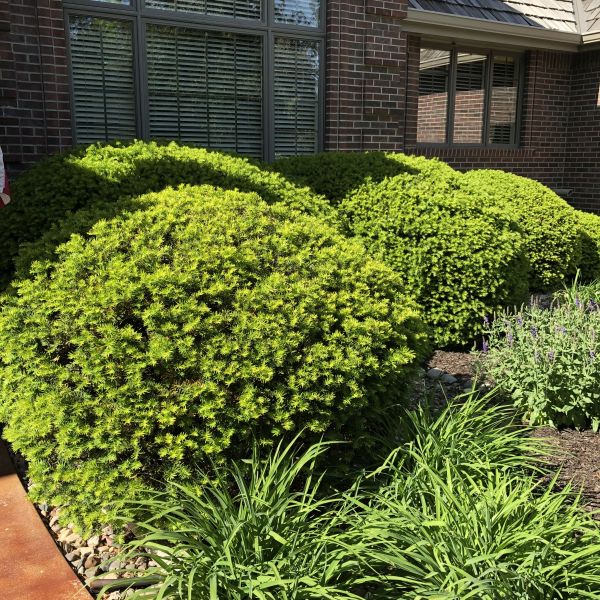
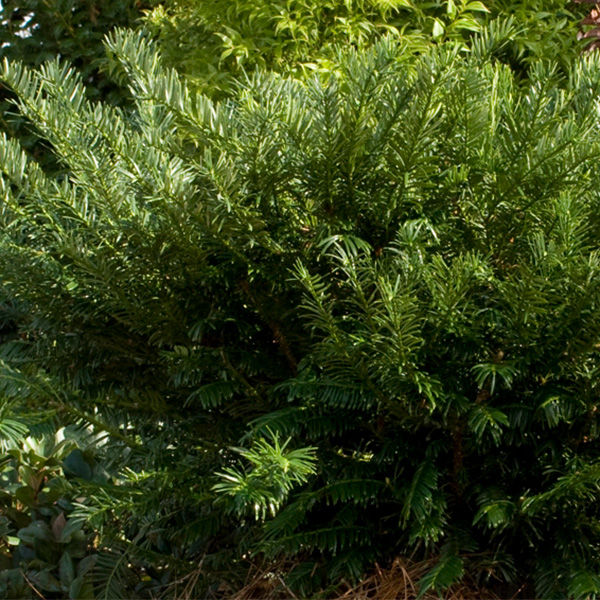
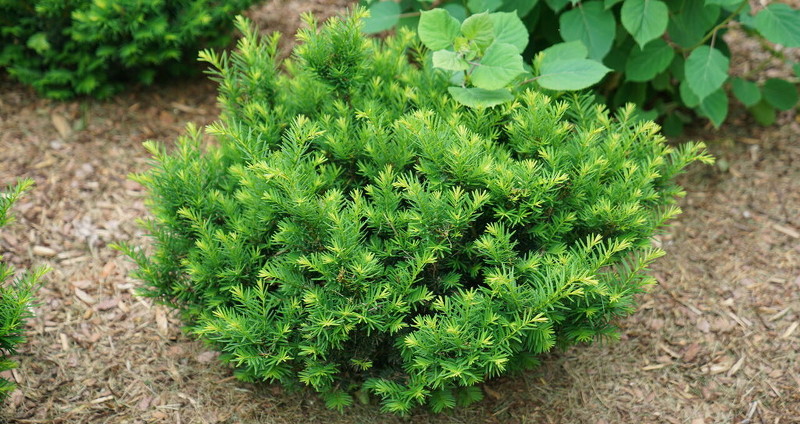
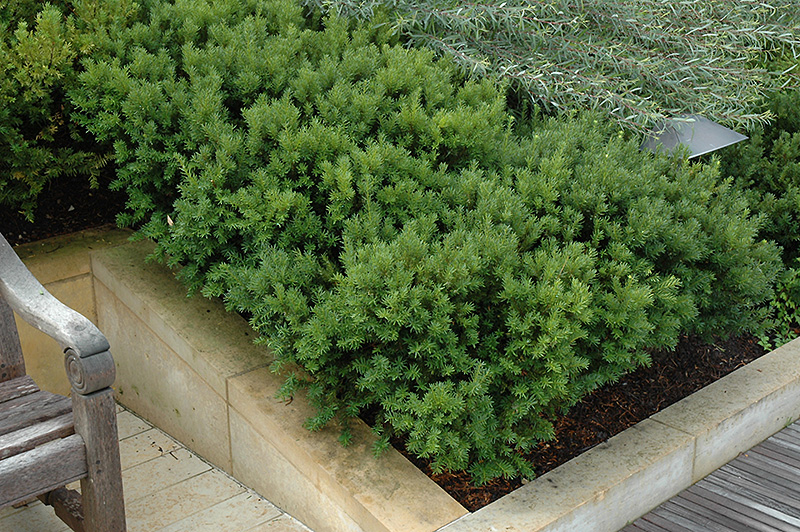
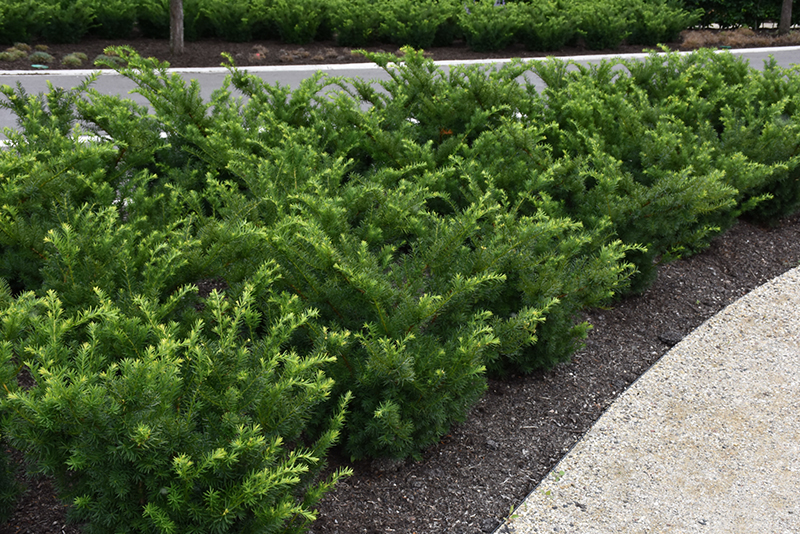
Yew
Yew shrubs belong to the genus Taxus and are evergreen plants known for their dense, dark green foliage and attractive red berries. Yews are native to various regions around the world, including Europe, North America, Asia, and Africa. These slow-growing shrubs are valued for their elegant appearance, fine-textured leaves, and ability to be pruned into various shapes and forms. Yew shrubs have been cultivated for centuries and have a long history of use in gardens, landscapes, and even as ornamental topiaries.

Common Types: There are several species and cultivars of yew shrubs, with some common ones including:
- Taxus baccata (English Yew): Native to Europe, this species is commonly used for hedging and topiary work.
- Taxus cuspidata (Japanese Yew): Native to Japan, this species is often used in Japanese gardens and landscapes.
- Taxus media (Hybrid Yew): A hybrid between Taxus baccata and Taxus cuspidata, combining the best qualities of both species.

Care Tips:
- Sunlight: Yew shrubs prefer partial to full sun. They can tolerate shade but will grow more vigorously with more sun exposure.
- Soil: Well-draining, fertile soil is ideal for yew shrubs. They can tolerate various soil types but prefer good drainage.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist, especially during the establishment phase. Once established, yew shrubs are relatively drought-tolerant.
- Mulching: Applying a layer of organic mulch around the base of the shrubs helps retain soil moisture and regulates temperature.
- Pruning: Yew shrubs respond well to pruning and can be shaped into formal hedges, topiaries, or left to grow as natural shrubs.
- Fertilization: Yew shrubs generally don't require heavy fertilization. A balanced fertilizer applied in the spring can support healthy growth.

Uses:
- Hedges and Screens: Yew shrubs are commonly used to create dense, formal hedges and screens in gardens and landscapes.
- Topiaries: Due to their slow growth and ability to be pruned, yew shrubs are popular choices for creating intricate topiaries and sculptural designs.
- Ornamental Specimens: Yew shrubs can be planted as individual ornamental specimens in gardens, adding elegance and structure to the landscape.
- Wildlife Attraction: The red berries of yew shrubs are attractive to birds and other wildlife, making them beneficial for supporting local ecosystems.
Yew shrubs are highly valued for their classic, timeless appeal and versatility in garden design. They have a natural tendency to form dense, compact growth, making them excellent choices for creating formal shapes and maintaining privacy. Their evergreen nature ensures year-round interest and provides a lush green backdrop for other garden plants. When planting yew shrubs, it's essential to be cautious of their toxic foliage and berries, which can be harmful if ingested. However, with proper care and consideration, yew shrubs can be valuable and beautiful additions to gardens and landscapes.
Item has been added to your cart.




