Ship to: 43215 Update
- Plants
- Shade Trees
- Fall Color
- Poplar Trees
Plants Filter
Current Filters
Mature Height
Sunlight
Plant Type
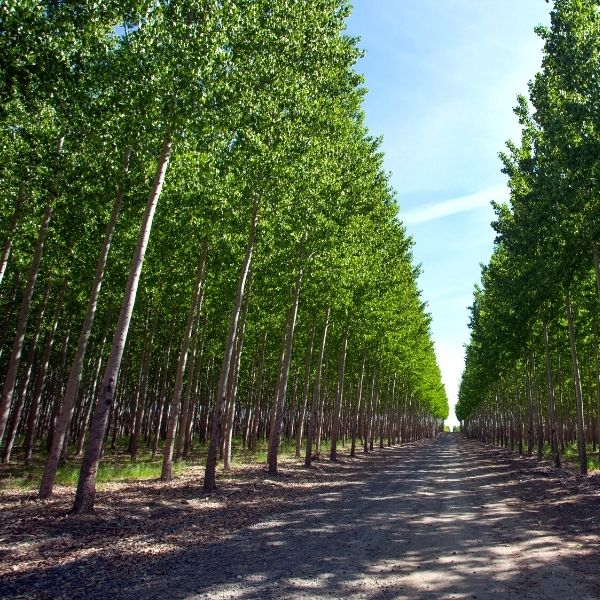
Poplar Trees
Poplar trees are a group of fast-growing deciduous trees belonging to the genus Populus in the Salicaceae family. These trees are widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere and are known for their rapid growth, tall and straight trunks, and heart-shaped leaves with serrated edges. Poplar leaves are often arranged alternately on the branches and can be variously colored, ranging from bright green to silver-white, depending on the species and variety. Poplar trees are commonly planted for their quick growth and their usefulness in a variety of applications.

Common Types: There are several species and hybrids of poplar trees, with some common ones including:
- Populus deltoides (Eastern Cottonwood): Native to North America, it is known for its triangular leaves and rapid growth.
- Populus tremula (European Aspen or Quaking Aspen): Found in Europe and parts of Asia, it has leaves that tremble and flutter in the wind.
- Populus nigra (Black Poplar): Native to Europe, it is known for its dark bark and diamond-shaped leaves.
- Populus alba (White Poplar): A species with silvery-white leaves, often used as a landscape tree.

Care Tips:
- Sunlight: Poplar trees prefer full sun to partial shade. They require adequate sunlight for optimal growth and development.
- Soil: Poplar trees can grow in a wide range of soil types but prefer well-draining, fertile soil.
- Watering: Young poplar trees may require regular watering to establish their root systems. Once established, they are relatively drought-tolerant.
- Mulching: Applying a layer of organic mulch around the base of the tree helps retain soil moisture and suppresses weed growth.
- Pruning: Prune poplar trees as needed to remove dead or diseased branches and to shape the tree's canopy. They tolerate heavy pruning and respond well to it.
- Fertilization: Poplar trees generally don't require heavy fertilization. A balanced fertilizer applied in the spring can support healthy growth.
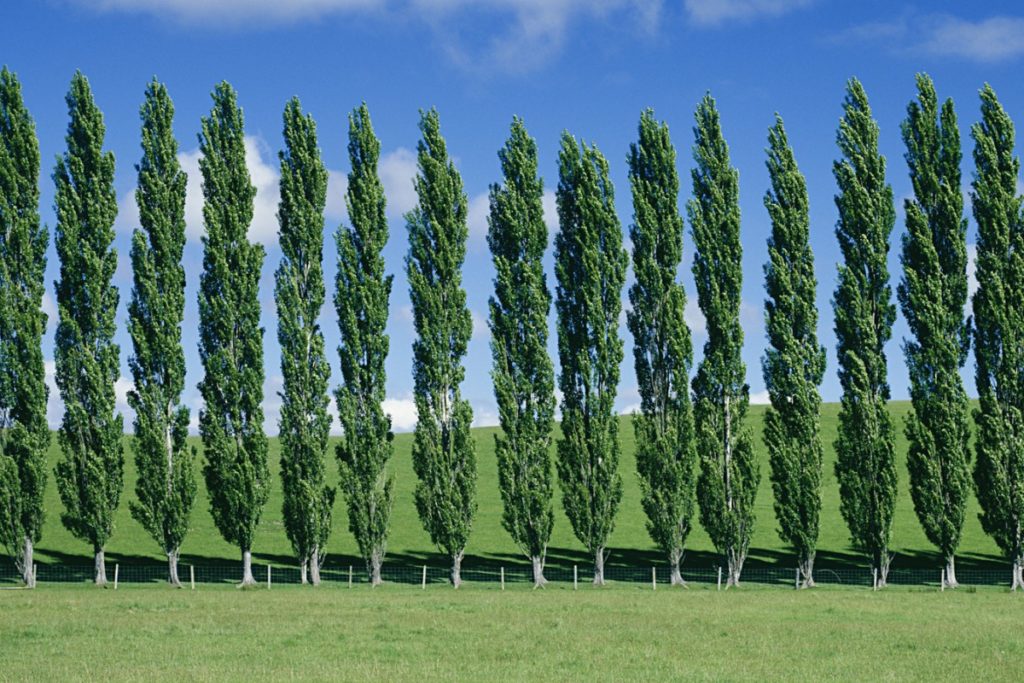

Uses:
- Rapid Shade: Poplar trees are popular choices for providing quick shade in landscapes due to their fast growth rate.
- Timber: Poplar wood is relatively soft and lightweight, making it suitable for a range of applications, including furniture, plywood, and boxes.
- Bioenergy: Poplar trees are sometimes grown as biomass crops for their potential use as a renewable energy source.
Poplar trees are valued for their rapid growth and versatility, making them useful in various settings. They are commonly used for quick landscaping projects, such as windbreaks, screens, and erosion control. Poplar wood, though not as dense or durable as some other hardwoods, is still valuable for certain applications due to its easy workability and affordability. Additionally, poplar trees play a role in environmental conservation, as they can be used in phytoremediation to help clean contaminated soils and waters.
Item has been added to your cart.



