Ship to: 43215 Update
Plants Filter
Current Filters
Mature Height
Sunlight
Plant Type
Cedars

Deodar Cedar Tree
Starting at $127
30% Off
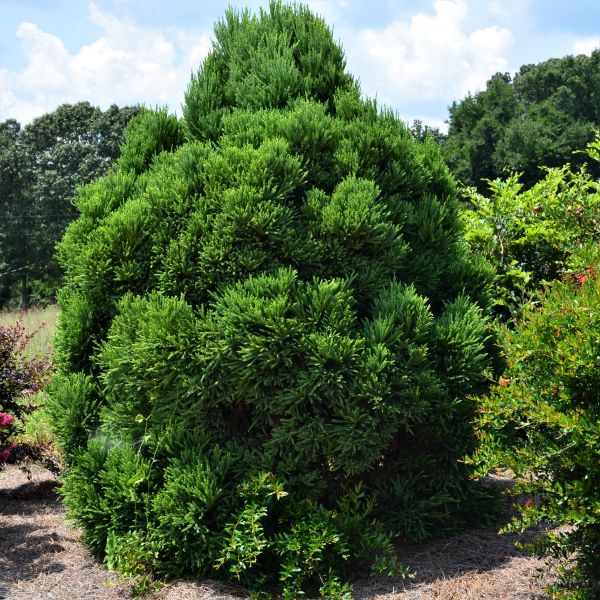

Chapel View Japanese Cedar
Out of Stock
30% Off
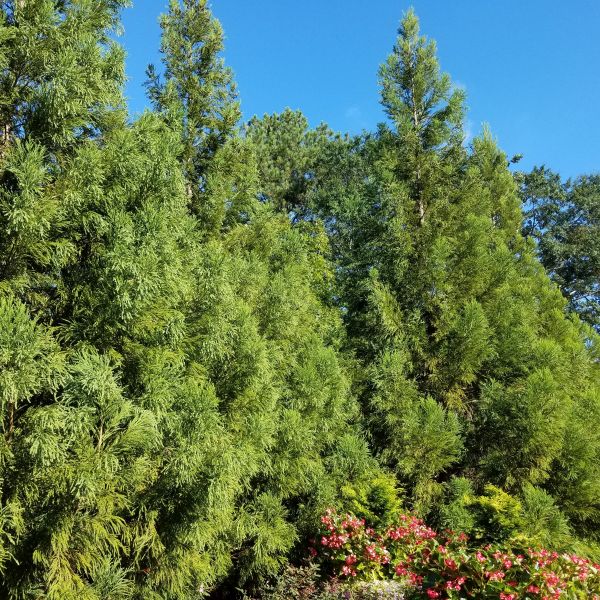

Cryptomeria Yoshino
Out of Stock
30% Off
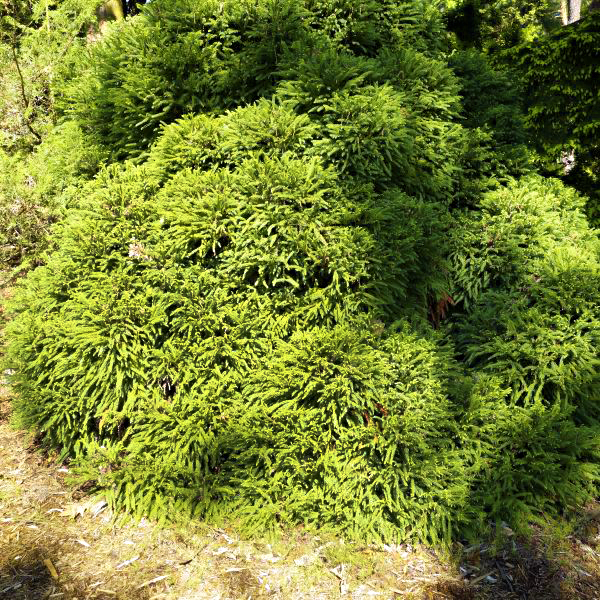

Dwarf Japanese Cedar
Out of Stock
30% Off

Eastern Red Cedar Tree
Out of Stock
30% Off

Eastern Red Cedar Tree
Out of Stock
30% Off

Yoshino Japanese Cedar Tree
Out of Stock
30% Off
Cedars
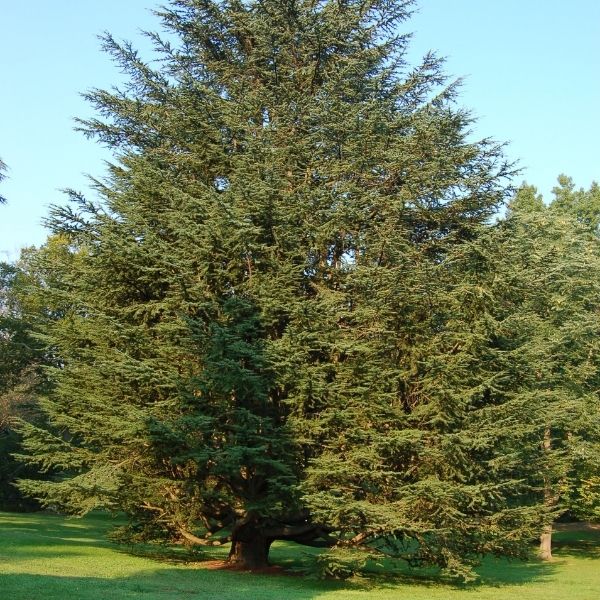
Cedar trees are a group of coniferous evergreen trees belonging to the family Pinaceae. There are several species of cedar trees, with some of the most common ones being the Eastern Red Cedar (Juniperus virginiana), Western Red Cedar (Thuja plicata), and the Atlantic White Cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides). These majestic trees are known for their tall, upright growth, pyramidal shape, and aromatic foliage. The leaves of cedar trees are needle-like and typically dark green in color. Cedar trees often produce cones, which contain the seeds and can vary in size and shape depending on the species.

Varieties: As mentioned earlier, some of the well-known cedar tree species include:
- Eastern Red Cedar (Juniperus virginiana): Native to eastern North America, this cedar species is commonly found in a wide range of habitats, including forests, open fields, and rocky slopes.
- Western Red Cedar (Thuja plicata): Native to western North America, this cedar species is admired for its large size, valuable wood, and aromatic foliage.
- Atlantic White Cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides): Native to the eastern United States, this cedar species is commonly found in swampy and wetland areas.

Care Tips:
- Sunlight: Cedar trees typically prefer full sun to partial shade. They thrive in locations with plenty of direct sunlight.
- Soil: Well-draining soil is essential for cedar trees. They can tolerate a range of soil types but prefer good drainage.
- Watering: Established cedar trees are usually drought-tolerant, but proper watering is essential during dry periods, especially when they are young and establishing their root systems.
- Mulching: Applying a layer of organic mulch around the base of the tree helps retain soil moisture and regulate temperature.
- Pruning: Cedar trees do not require much pruning, but occasional maintenance may be needed to remove dead or diseased branches and to shape the tree if desired.
- Fertilization: In most cases, cedar trees do not require heavy fertilization. If needed, a balanced fertilizer can be applied in spring to support healthy growth.

Uses:
- Ornamental Trees: Cedar trees are commonly grown as ornamental trees in gardens and landscapes, providing year-round greenery and an attractive presence.
- Privacy Screens and Windbreaks: Cedar trees are often used as privacy screens and windbreaks due to their tall and dense growth habit.
- Wood Production: Some cedar species, like the Western Red Cedar, are highly valued for their durable and aromatic wood, which is used for various purposes, including construction, furniture, and decorative items.
Cedar trees are esteemed for their beauty, longevity, and various practical uses. As iconic trees in many landscapes, they bring a sense of sturdiness and timelessness to the surroundings. Whether standing tall in a forest, providing privacy in a backyard, or being admired for their scent and appearance in a garden, cedar trees are cherished additions to any environment. With proper care and appreciation for their unique qualities, cedar trees can thrive and become a cherished part of the natural beauty around us.
Item has been added to your cart.

