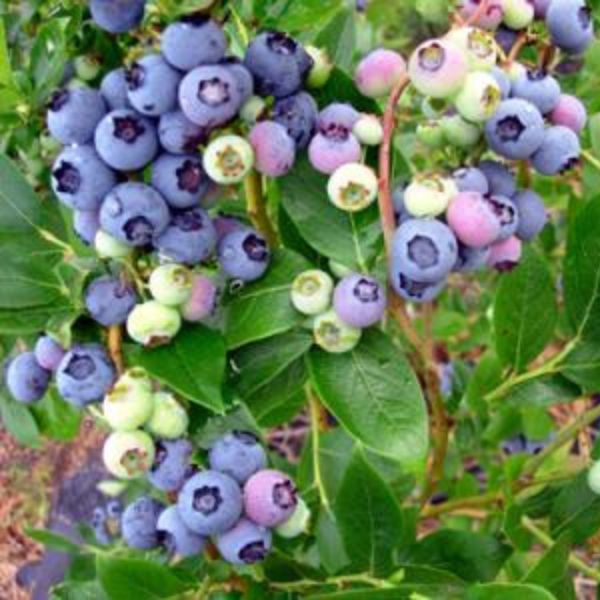
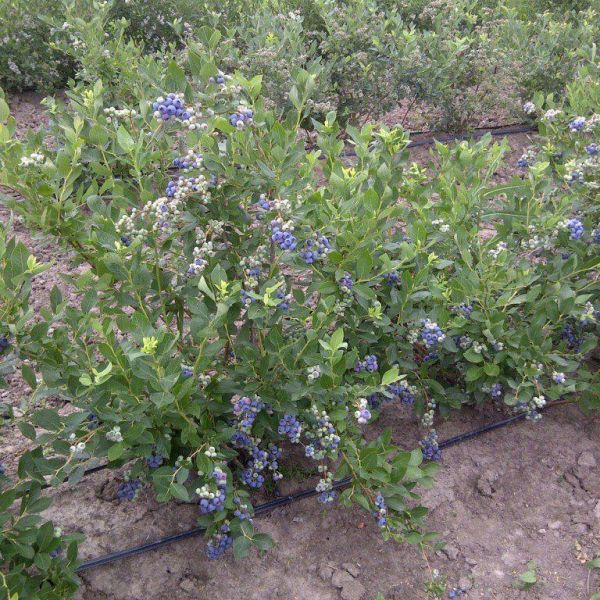
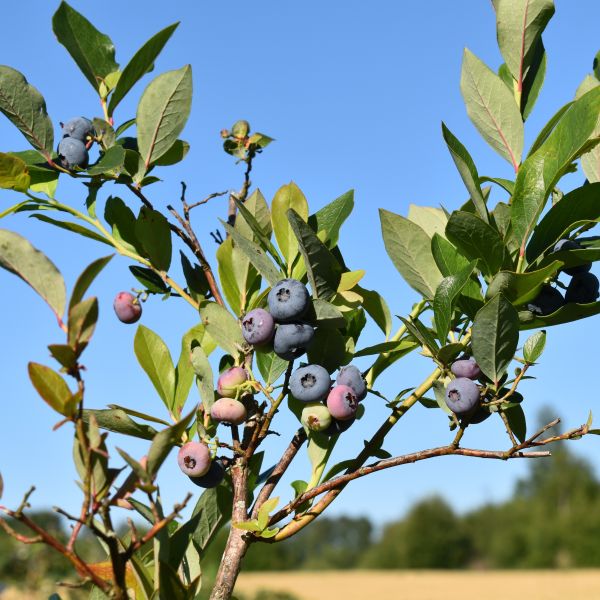
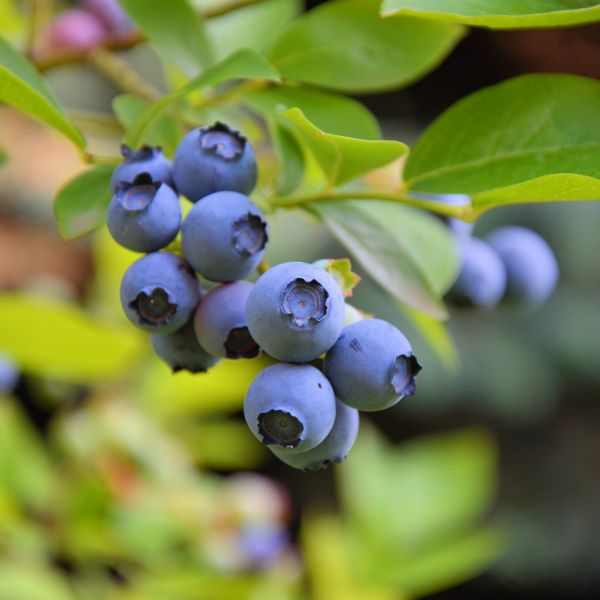
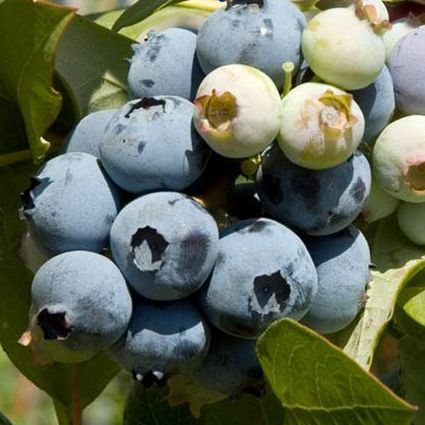
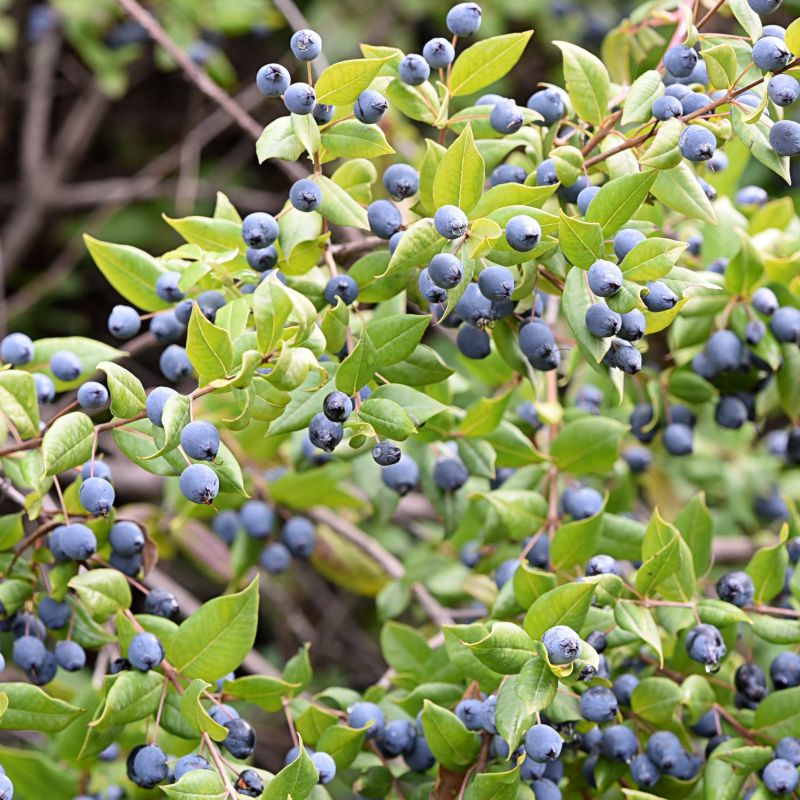
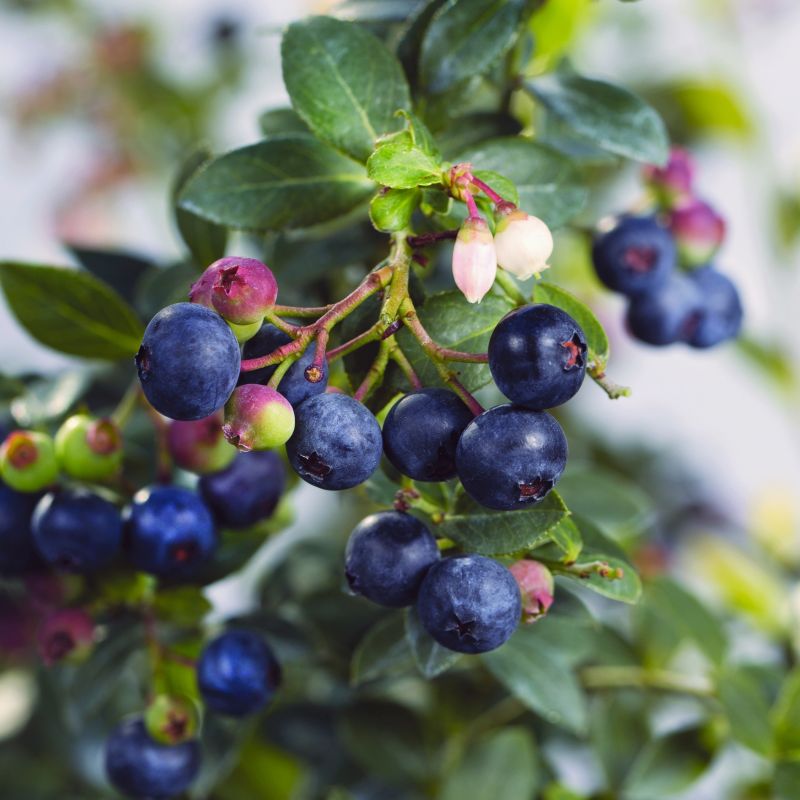
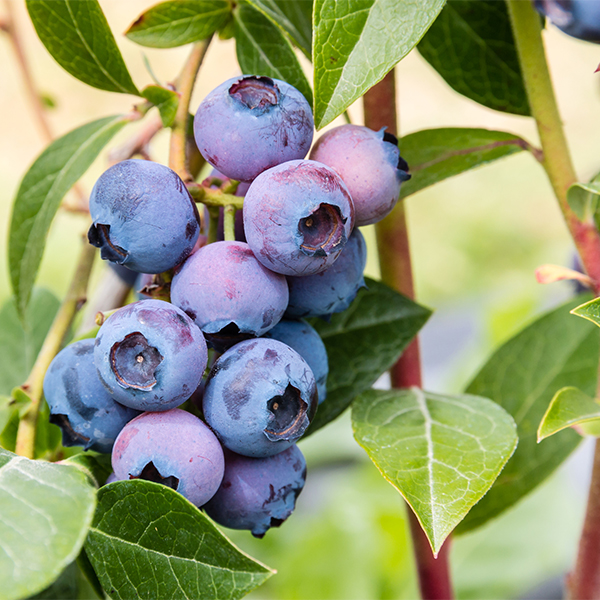
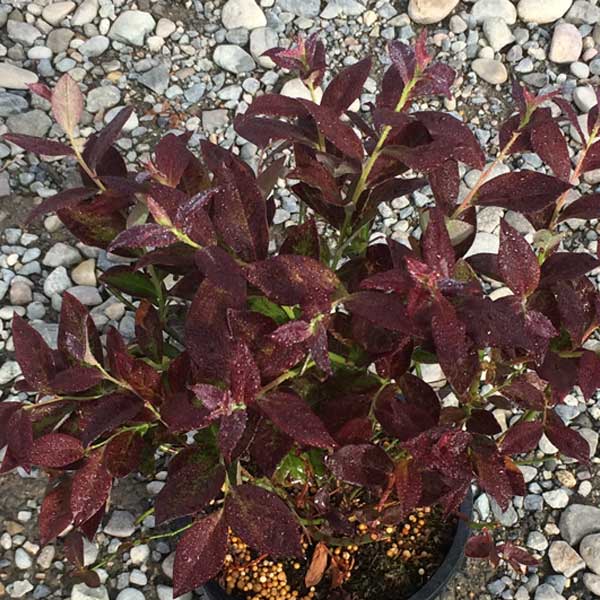
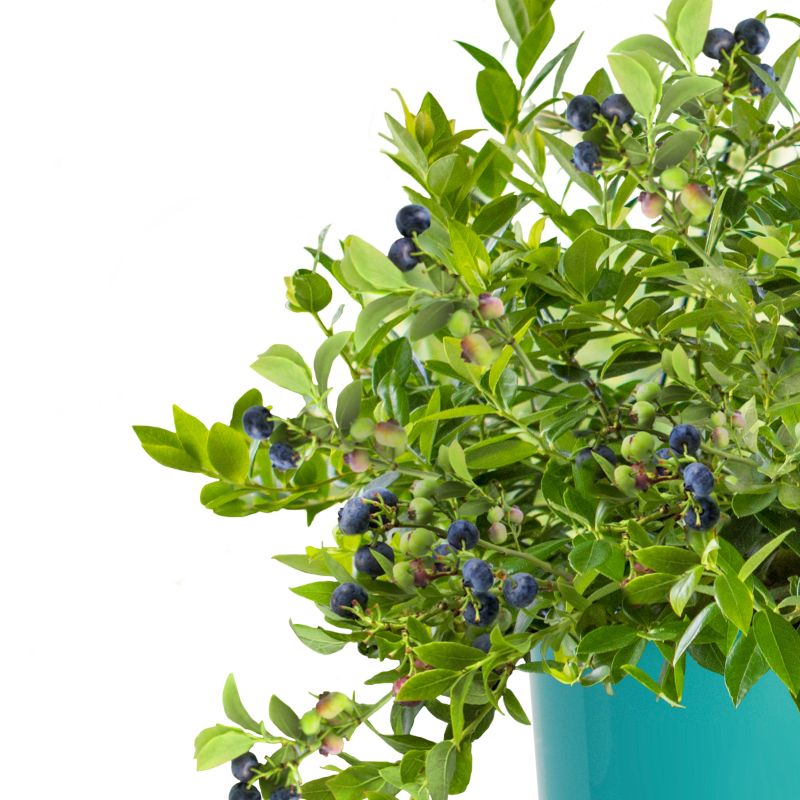
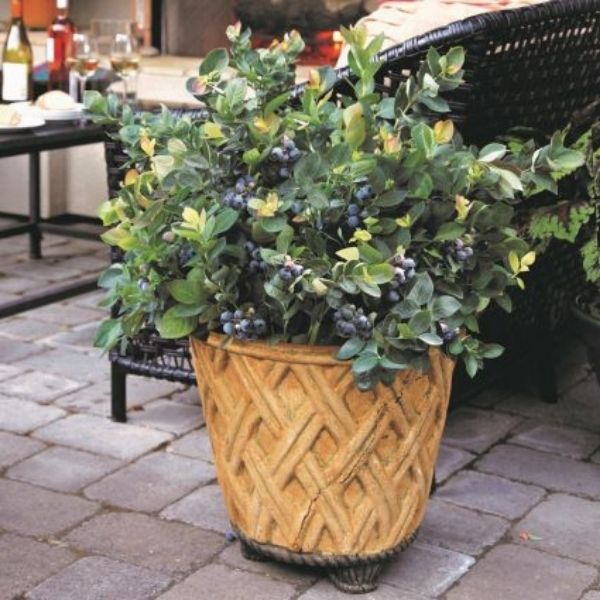
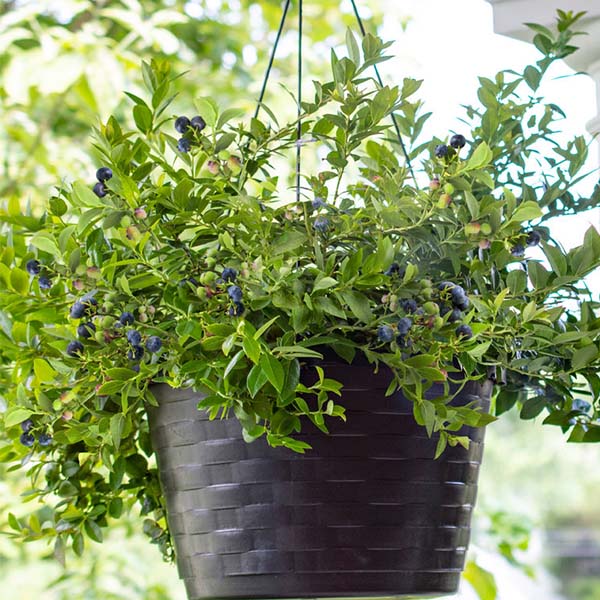
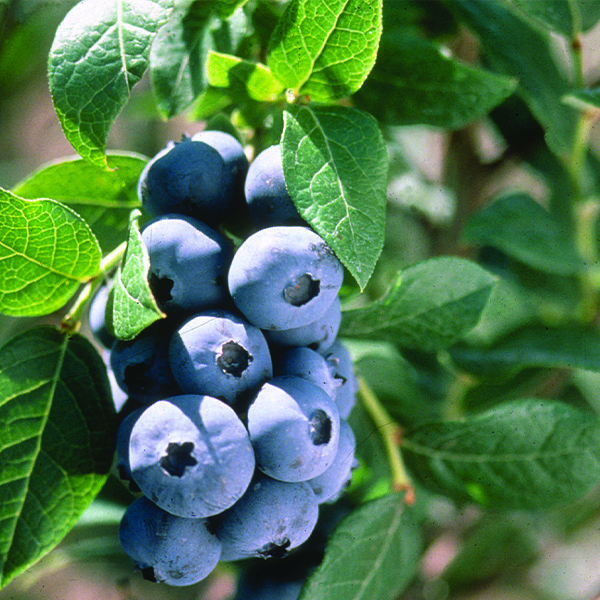
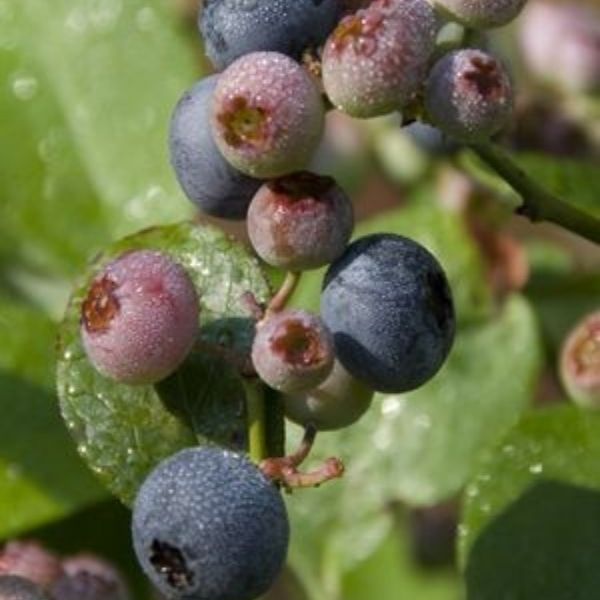
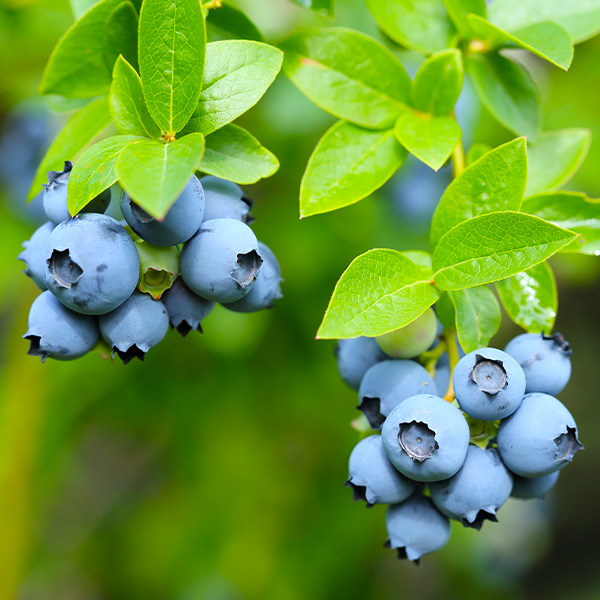
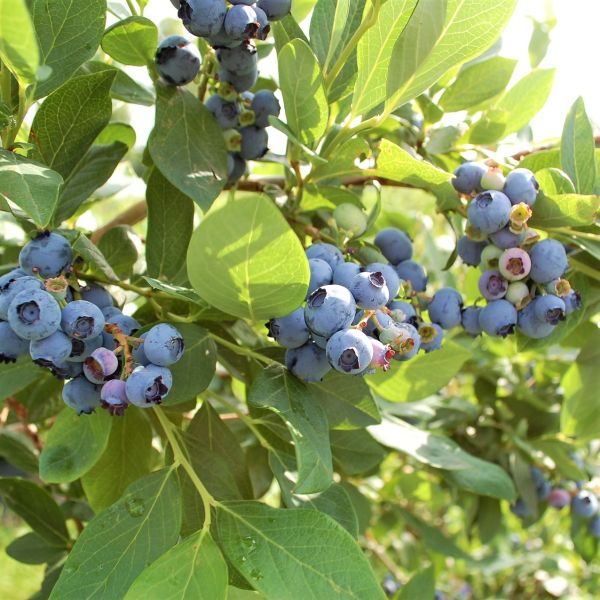
Duke Blueberry
Vaccinium corymbosum 'Duke'
20 reviews
Duke Blueberry
Vaccinium corymbosum 'Duke'
20 reviews
- 1 Gallon
- 2.5 Gallon
We are sorry, product is currently out of stock due to seasonal availability. Please check the "Related plants available in your area" section below
Why Duke Blueberry?
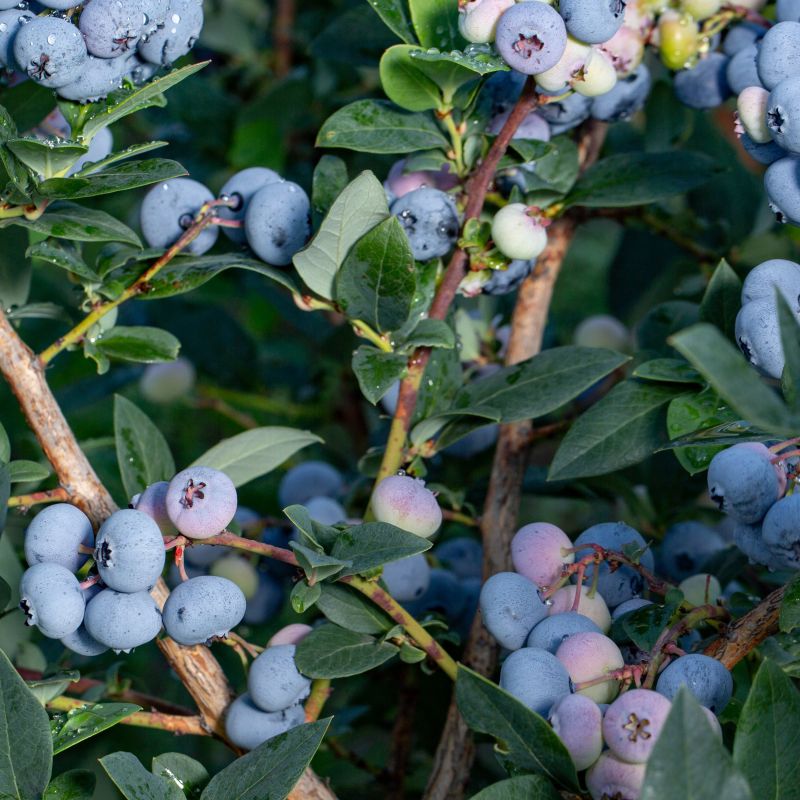
Duke Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum 'Duke') is a popular variety due to its numerous advantages. It is known for its high yield of large, flavorful berries that ripen early in the season. The plant is vigorous and disease-resistant, making it a reliable choice for home gardeners and commercial growers. Duke Blueberry's adaptability to various climates and its ability to self-pollinate further contribute to its appeal.
Related plants available in your area
Sunlight
Duke Blueberry requires full sun to thrive and produce an abundant harvest.
Watering
Duke blueberries have moderate watering requirements. They prefer consistently moist soil, but they can tolerate brief periods of dryness. Regular watering is recommended, especially during the growing season, to ensure optimal fruit production.
Fertilizing
Duke Blueberry requires a balanced fertilizer with an NPK ratio of 10-10-10 or 14-14-14. Additionally, it benefits from organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure. Regular fertilization should be done during the growing season to promote healthy
Duke Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum 'Duke')
The Duke Blueberry, scientifically known as Vaccinium corymbosum 'Duke', is a deciduous shrub belonging to the Ericaceae family. It is a popular cultivar of blueberry that is highly regarded for its excellent taste and abundant harvest.
Plant Characteristics
- Size: Duke Blueberry typically grows to a height of 4-6 feet and has a spread of 3-4 feet, forming a compact, upright bush with a rounded shape.
- Foliage: The leaves are dark green, oval-shaped, and have a glossy appearance. In autumn, they turn into vibrant shades of yellow, orange, and red, providing beautiful fall color.
- Flowers: In spring, Duke Blueberry produces small, white or pinkish, bell-shaped flowers that are both attractive and beneficial to pollinators.
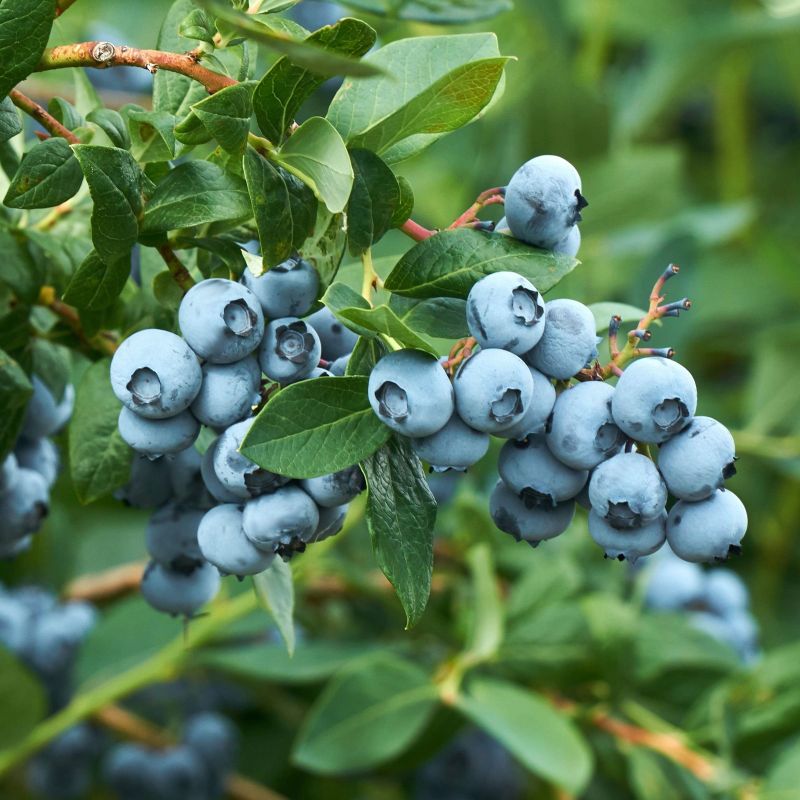
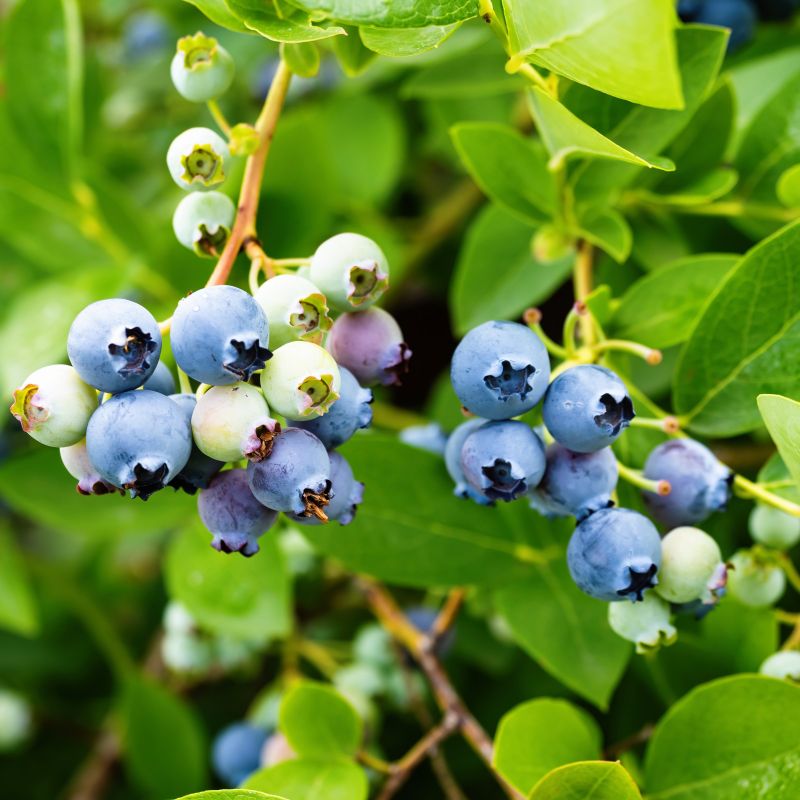
- Fruit: The real star of this blueberry variety is its delicious fruit. The berries are large, plump, and have a deep blue color with a silvery bloom. They offer a sweet flavor with a subtle tang, perfect for fresh consumption or various culinary applications.
Growth Requirements
- Sun Exposure: Duke Blueberry thrives in full sun, but it can also tolerate partial shade.
- Soil: It prefers well-draining, acidic soil with a pH range of 4.5 to 5.5. Adding organic matter and creating a mulch layer around the base of the plant can help maintain soil moisture.
- Watering: Blueberries have moderate water requirements. Regular watering, especially during dry periods, is necessary to ensure optimal growth and fruit development.
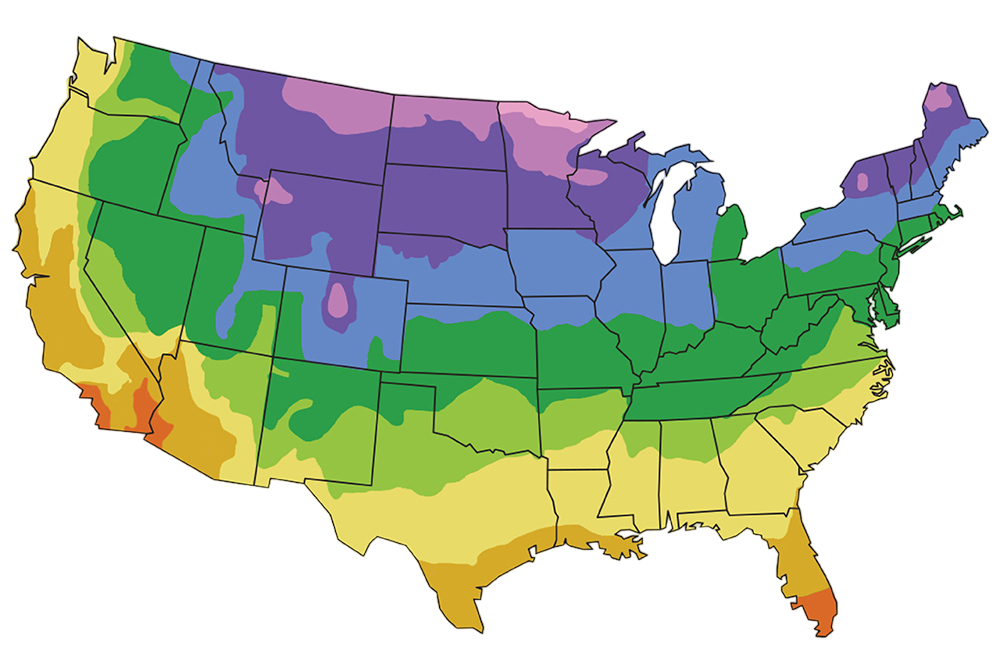
- Hardiness Zones: This variety is winter-hardy and suitable for planting in USDA Hardiness Zones 4-7.
- Pollination: While Duke Blueberry is partially self-fertile, planting multiple blueberry varieties nearby can increase fruit yield. Cross-pollination between different cultivars is beneficial.
- Pruning: Pruning should be carried out during the dormant season to remove dead or damaged branches and maintain a healthy shape. It also encourages new growth and enhances fruit production.
- Pests and Diseases: Duke Blueberry is generally resistant to many pests and diseases. However, occasional issues with birds, aphids, mites, or fungal diseases might require appropriate preventive measures.
Uses and Culinary Delights
The bountiful harvest of Duke Blueberry is not only rewarding for gardeners but also offers a wide range of culinary possibilities:
- Enjoy the fresh berries as a healthy and delicious snack.
- Include them in fruit salads, smoothies, or breakfast cereals.
- Bake them into pies, muffins, pancakes, or cakes.
- Preserve them by making jams, jellies, or sauces.
- Freeze the berries to enjoy throughout the year.
The Duke Blueberry is an exceptional choice for both home gardeners and commercial growers, offering abundant harvests of delectable fruit and ornamental value with its attractive foliage and flowers. Planting this cultivar is sure to enhance any landscape while satisfying your taste buds.
Plant Information:
| Botanical Name: | Vaccinium corymbosum 'Duke' |
| USDA Zones: | 4 - 7 |
| Exposure: | Full Sun |
| Soil Needs: | Widely Adaptable |
| Mature Height: | 4 - 6 feet |
| Mature Spread: | 5 - 8 feet |
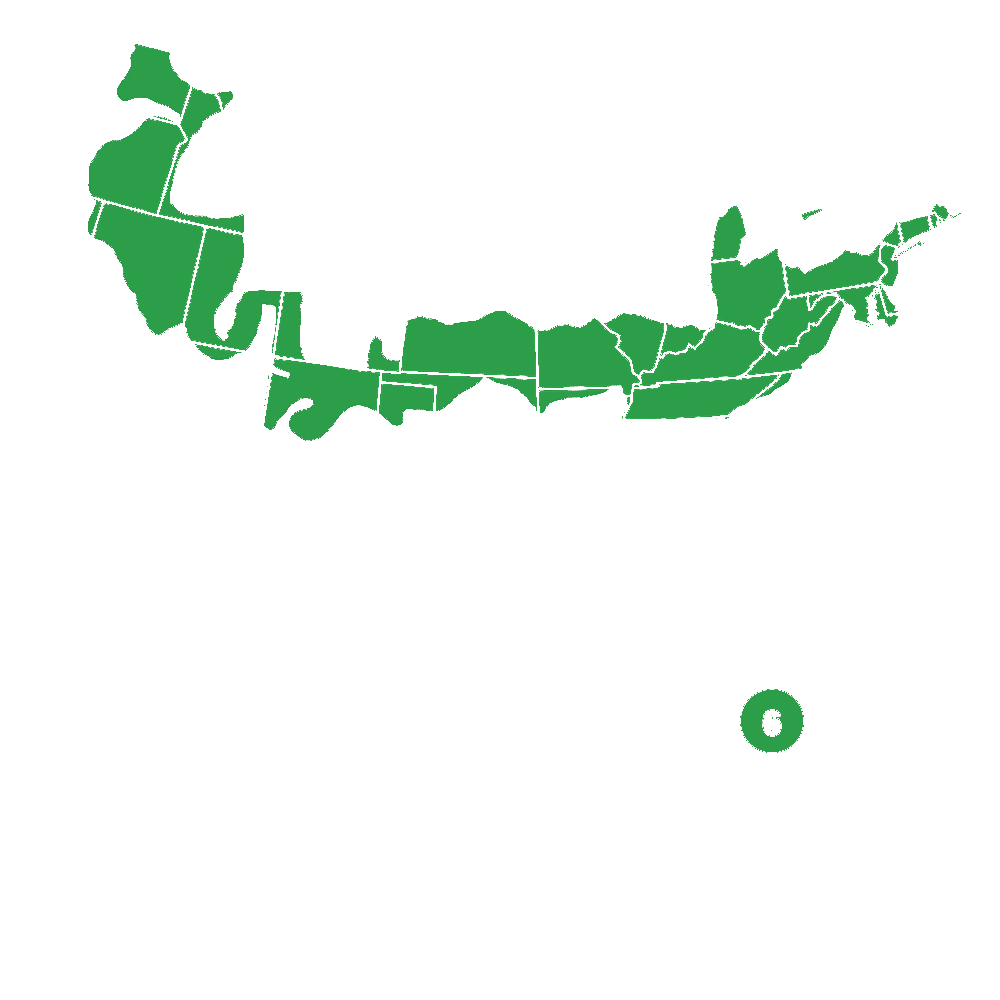
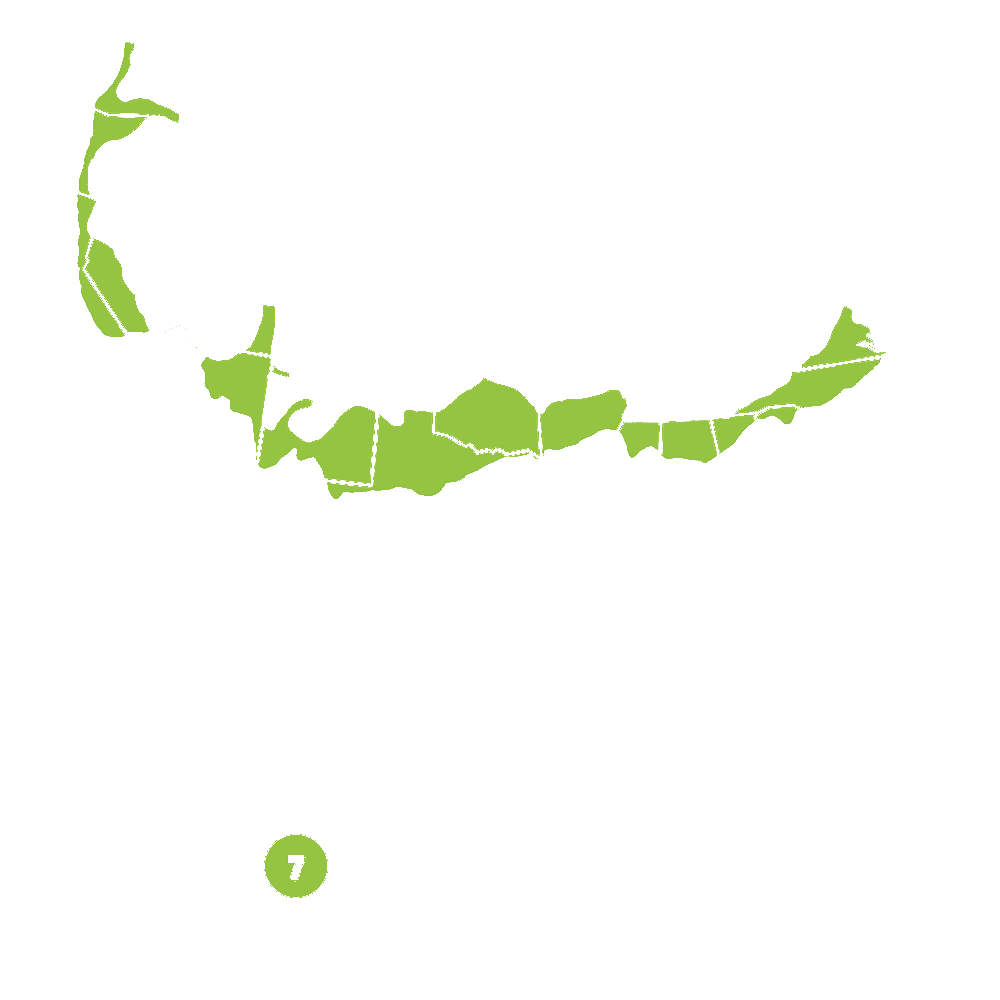
Pollination Info
Pollination Information for Duke Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum 'Duke')
Duke Blueberry is a variety of highbush blueberry, Vaccinium corymbosum. Blueberries are self-fertile, but usually produce higher yields if cross-pollinated by another compatible blueberry cultivar.
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the male reproductive organs (anthers) to the female reproductive organs (stigma) of flowers. This process is essential for the fruit to develop through fertilization.
Basic Pollination Facts:
- Plant Type: Highbush blueberry
- Botanical Name: Vaccinium corymbosum 'Duke'
- Pollination Type: Self-fertile (able to set fruit with its own pollen) but benefits from cross-pollination
Cross-Pollination:
Cross-pollination occurs when pollen is transferred between two different blueberry plants of compatible cultivars. Cross-pollination increases the fruit set and improves the quality of the berries.
Recommended Pollinators:
To achieve higher yields, it is recommended to plant a different blueberry cultivar near Duke Blueberry. Ideally, choose another highbush blueberry variety that blooms around the same time as Duke Blueberry. Some compatible cultivars commonly recommended as pollinators for Duke Blueberry include:
- Bluecrop
- Bluejay
- Patriot
- Blueray
- Jersey
Pollination Method:
The primary pollinators of blueberries are bees, especially honeybees and bumblebees. These insects transfer pollen while foraging for nectar and pollen from the flowers. Providing a suitable habitat and attracting bees to your garden can increase the chances of successful pollination. Avoid the use of insecticides during bloom as it may harm the pollinators.
You can also manually assist in pollination by using a small brush or cotton swab to transfer pollen from one flower to another during the flowering season.
Pollination Time:
The flowering time of Duke Blueberry typically occurs in spring, usually between April and May. This is the crucial period for pollination. It is important to have compatible pollinator plants blooming simultaneously to ensure successful cross-pollination.
Remember, while Duke Blueberry is self-fertile, planting a compatible pollinator nearby can increase fruit yields and improve overall fruit quality. Bees play a critical role in the natural pollination process, so it's essential to create a bee-friendly environment in your garden.
FAQ
Duke Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum 'Duke') - FAQs
1. What is Duke Blueberry?
Duke Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum 'Duke') is a variety of highbush blueberry known for its large and flavorful berries. It is a deciduous shrub that belongs to the Ericaceae family.
2. How tall does Duke Blueberry grow?
Duke Blueberry can grow between 4 to 6 feet in height, making it a compact variety suitable for small gardens or containers.
3. What is the hardiness zone for Duke Blueberry?
Duke Blueberry is hardy in zones 5-7. It can tolerate colder temperatures but may require extra protection in extreme winter conditions.
4. When do Duke Blueberry plants bloom?
The Duke Blueberry plant typically blooms in late spring to early summer. It produces small, white or pink bell-shaped flowers that are attractive to bees and other pollinators.
5. When can I harvest the berries?
The berries of Duke Blueberry usually ripen in mid to late summer, depending on the climate and growing conditions. You can harvest them when they are fully blue and easily detach from the plant with a gentle tug.
6. How should I care for Duke Blueberry?
Here are some care tips for Duke Blueberry:
- Plant it in well-drained, acidic soil with a pH level between 4.5 to 5.5.
- Choose a location with full sun or partial shade.
- Water regularly, especially during dry spells, to keep the soil consistently moist.
- Apply mulch around the base of the plant to retain moisture and suppress weed growth.
- Prune the plant in late winter or early spring to remove dead or damaged branches and maintain its shape.
- Fertilize annually in early spring using an acidic fertilizer formulated for blueberries.
- Protect the plant from birds by covering it with bird netting during the fruiting season.
7. Can Duke Blueberry be grown in containers?
Yes, Duke Blueberry is suitable for container gardening. Use a large pot with drainage holes, and ensure the soil is acidic and well-drained. Place the container in a sunny spot, and provide regular watering and fertilization for optimum growth.
8. Are Duke Blueberries self-pollinating?
No, Duke Blueberries are not self-pollinating. It is recommended to plant multiple blueberry varieties near each other to ensure cross-pollination and enhance fruit production.
9. How can I prevent or control pests and diseases?
Common pests that may affect Duke Blueberry include aphids, blueberry maggot, and fruitworms. Regularly inspect the plant for signs of infestation and use appropriate organic insecticides or insecticidal soaps if necessary. Some common diseases include powdery mildew, root rot, and leaf spot. Ensure proper air circulation, avoid overwatering, and apply fungicides as required.
10. How long does Duke Blueberry plant live?
With proper care and maintenance, Duke Blueberry plants can live around 10 to 20 years, providing you with delicious berries for many seasons to come.
Planting & Care
Planting & Care for Duke Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum 'Duke')
Planting:
- Choose a location with full sun exposure (at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day).
- Ensure the soil is acidic (pH level between 4 and 5.5), well-draining, and rich in organic matter.
- Dig a hole that is twice as wide and as deep as the root ball of the Duke Blueberry plant.
- Carefully remove the plant from its container and gently loosen the roots.
- Place the plant in the hole, ensuring that the top of the root ball is level with the soil surface.
- Backfill the hole with soil, firming it gently to eliminate any air pockets.
- Water the plant thoroughly after planting to settle the soil.
Care:
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Blueberries require about 1-2 inches of water per week. Water deeply and thoroughly, especially during dry spells.
- Fertilization: Apply a balanced, slow-release fertilizer specifically formulated for acid-loving plants in early spring. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer packaging for application rates.
- Pruning: Prune Duke Blueberry plants during late winter or early spring. Remove any dead, damaged, or crossing branches. Thin out the center of the plant to improve airflow and sunlight penetration.
- Pollination: Blueberries are self-fertile, but cross-pollination with another variety can increase fruit production. Planting multiple blueberry varieties nearby is recommended to ensure better pollination.
- Mulching: Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the plant to help conserve moisture, regulate soil temperature, and suppress weed growth. Pine needles, wood chips, or pine bark are ideal mulch options.
- Pests and Diseases: Watch out for common blueberry pests such as aphids, leafhoppers, and blueberry maggots. Regularly inspect the plant for signs of disease, including fungal infections like powdery mildew and botrytis blight. Treat any issues promptly with appropriate pesticides or fungicides.
By following these planting and care guidelines, you can ensure healthy growth and abundant harvest from your Duke Blueberry plant.
Check Out These Verified Customer Reviews:
Customer Reviews
4.7 out of 5 based on 20 reviews
Thank you! Your review has been submitted.
The website was easy to navigate and order from.
Customer service was excellent. They were responsive and helpful with my inquiries.
I was impressed by the freshness and taste of the Duke Blueberries. Highly recommend!
Item has been added to your cart.