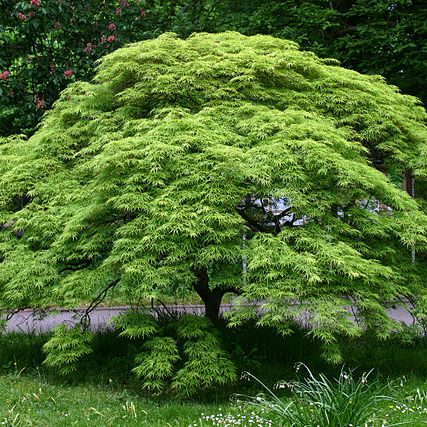
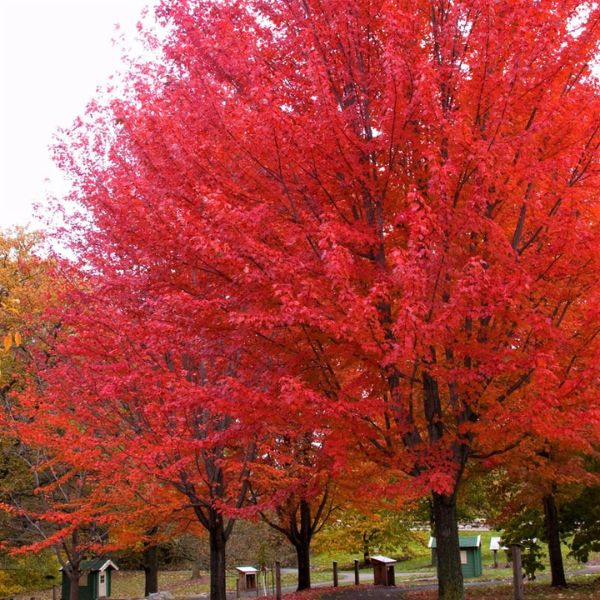
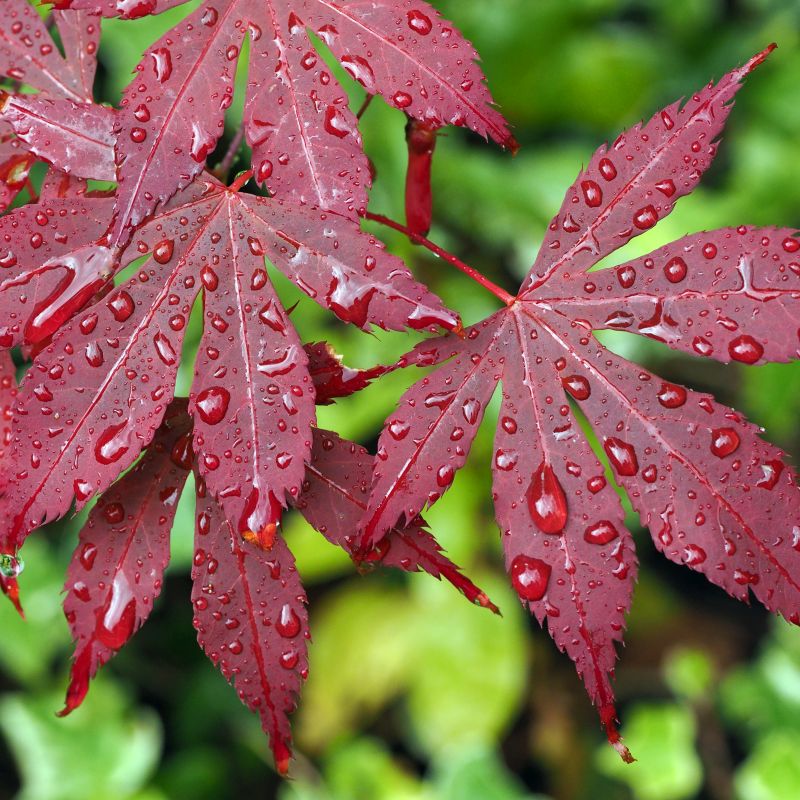
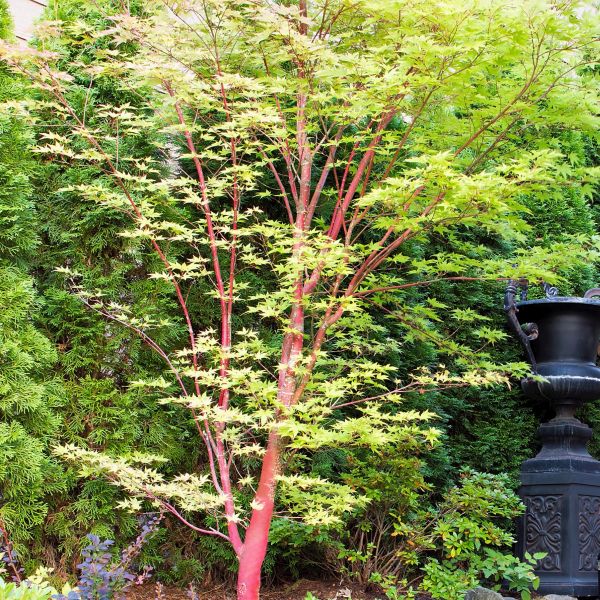
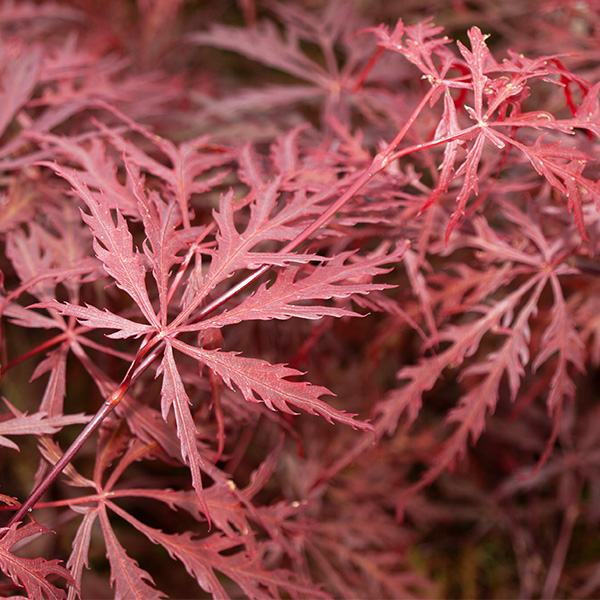
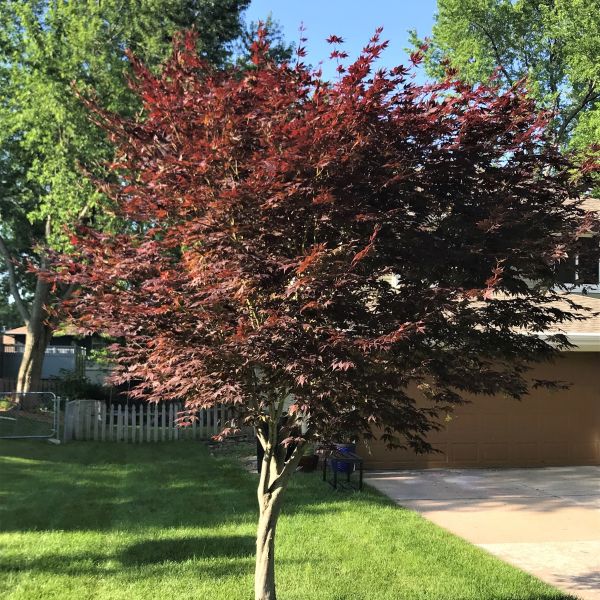
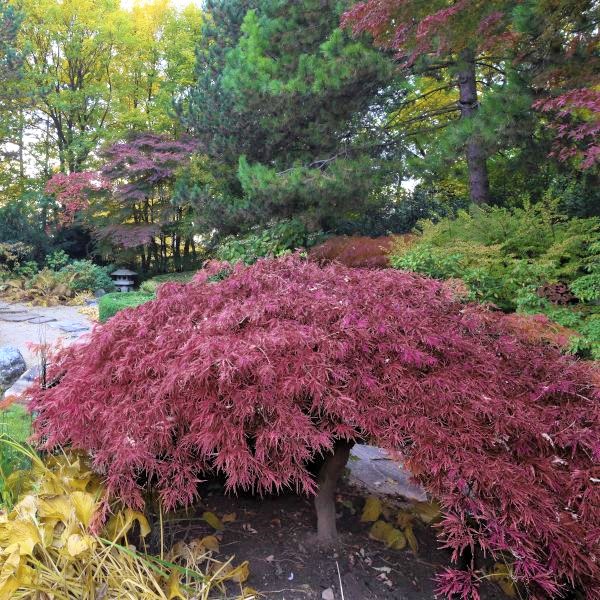
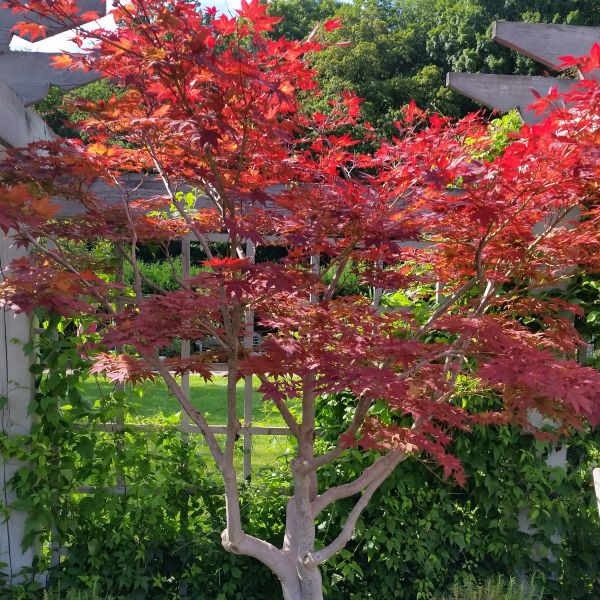
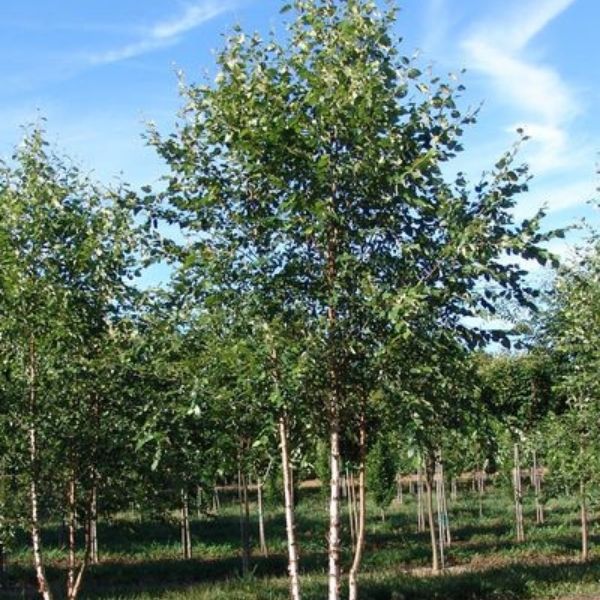
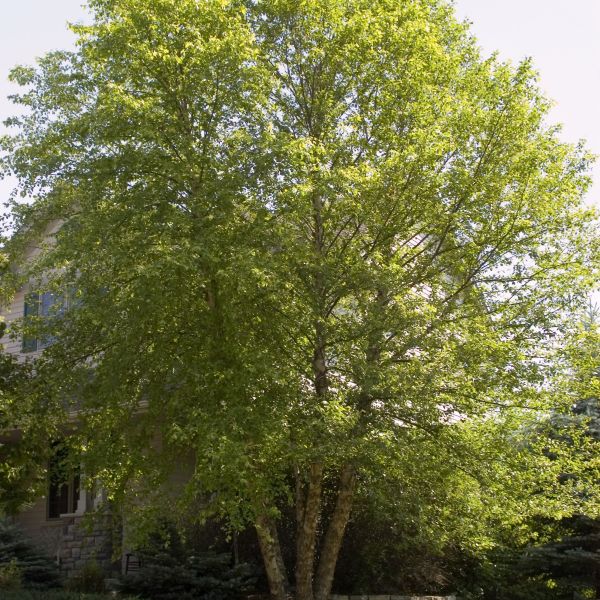
Japanese Maple
Acer Palmatum
Japanese Maple
Acer Palmatum
6 ft
Why Japanese Maple?
People who loved this plant also bought
Sunlight
Japanese maples prefer partial shade or filtered sunlight, especially during the hottest part of the day. They can tolerate some direct sunlight, but too much can scorch their delicate leaves.
Watering
Japanese Maple trees require regular watering, especially during the first few years of growth. They prefer moist, well-drained soil, but are sensitive to overwatering. It is important to keep the soil evenly moist, without allowing it to become waterlogge
Fertilizing
Japanese Maples prefer well-draining soil that is slightly acidic. They benefit from a balanced fertilizer application in early spring and late summer. A slow-release, 10-10-10 NPK (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) fertilizer is often recommended for h
Best grown in moist, organically rich, slightly acidic, well-drained soils in full sun to part shade. Grows well in sandy loams. May be grown in full sun in the northern parts of its growing range, but prefers some part afternoon shade in the southern parts (including St. Louis) of its growing range. New foliage may scorch in full sun locations in hot summers areas, particularly if soils are not kept consistently moist. Mulch helps retain soil moisture and keep roots cool.
Plant Information:
| Botanical Name: | Acer Palmatum |
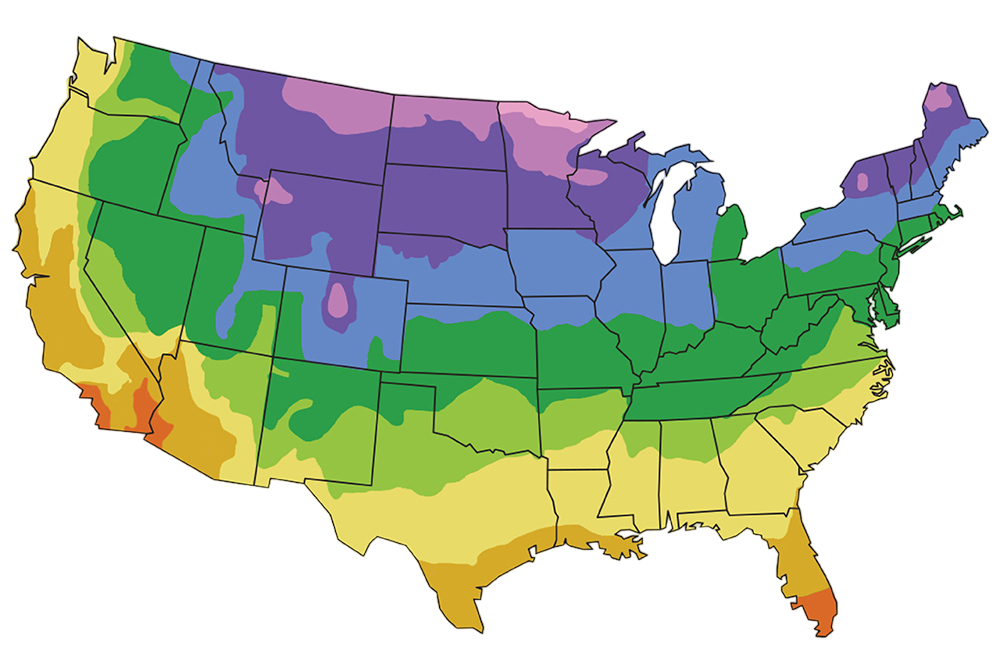
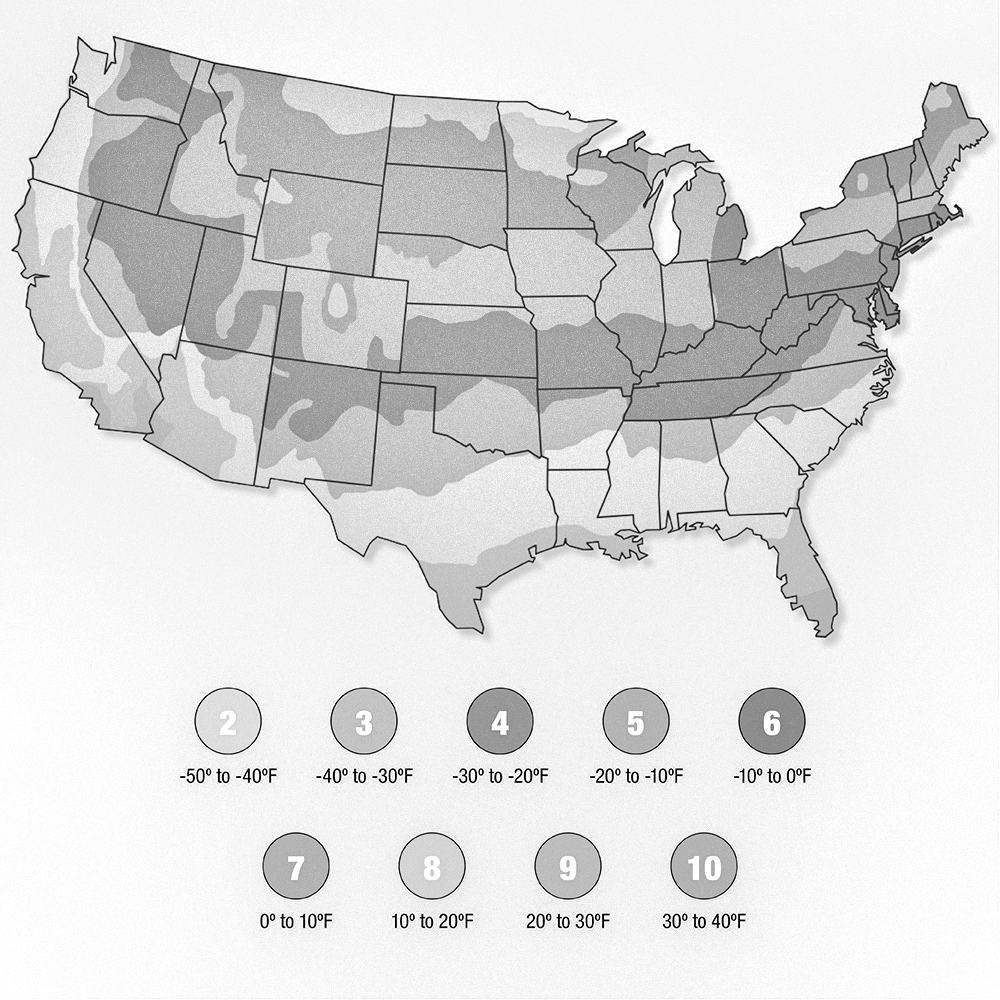
| USDA Zones: | 5a-9a |
| Growth Habit: | Rounded |
| Evergreen / Deciduous: | Deciduous |
| Color/Foliage: | Green |
| Water: | Regular |
| Exposure: | Full sun-Mostly Shade |
| Soil Needs: | Well-Drained,Rich |
| Mature Height: | 15'-20' |
| Mature Spread: | 15' |
Pollination Info
Pollination Info for Japanese Maple (Acer Palmatum)
Pollination Method:
Japanese Maple (Acer Palmatum) is primarily pollinated by wind.Male and Female Flowers:
Japanese Maple flowers are separated into male and female flowers. The male flowers produce pollen, while the female flowers contain the ovary.Flowering Season:
Japanese Maple typically blooms in the spring, usually in April or May, depending on the specific cultivar and location.Pollination Process:
During the flowering season, the male flowers release abundant pollen into the air. The lightweight pollen grains are carried by the wind to nearby female flowers. When the pollen reaches the stigma of the female flowers, fertilization occurs.Fruit Development:
Once fertilized, the ovary of the female flowers develops into a fruit called a samara. The samaras are winged seeds that are characteristic of the maple family. They are often shaped like small helicopters, which helps in their dispersal by wind.Seed Dispersal:
When the samaras are mature and dry, they detach from the tree and are carried away by the wind. The winged structure helps the samaras to glide and travel to new locations, aiding in the dispersal and propagation of the Japanese Maple species.Pollinator Considerations:
While Japanese Maples primarily rely on wind for pollination, it is still beneficial to attract insects like bees and butterflies to the garden. These insects can inadvertently assist in the pollination process, increasing the chances of successful seed production.FAQ
Japanese Maple (Acer Palmatum) FAQ
Q: What is a Japanese Maple (Acer Palmatum)?
A: Japanese Maple, scientifically known as Acer Palmatum, is a species of deciduous tree native to Japan, Korea, and China. It is widely cultivated around the world for its vibrant foliage and attractive form.
Q: How tall can a Japanese Maple tree grow?
A: Japanese Maple trees vary in size depending on the variety. Some cultivars can grow up to 25 feet tall, while others remain small and compact, reaching only 3-4 feet in height.
Q: What is the ideal growing zone for Japanese Maple?
A: Japanese Maples thrive in USDA hardiness zones 5-8. They prefer cool temperate climates and are not well-suited for extremely hot or cold regions.
Q: When should I plant a Japanese Maple tree?
A: The best time to plant a Japanese Maple tree is during early spring or fall when the temperatures are mild and the soil is workable. Avoid planting during hot summer months or freezing winters.
Q: How much sunlight does a Japanese Maple tree need?
A: Japanese Maples prefer partial shade or dappled sunlight. They can tolerate morning sun but should be protected from intense afternoon sun, which can scorch their delicate leaves.
Q: What type of soil is suitable for Japanese Maple?
A: Japanese Maples prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. A mixture of loam, sand, and peat moss works well. Avoid heavy clay soils that retain water.
Q: How often should I water a Japanese Maple tree?
A: Japanese Maples require regular watering, especially during dry periods. Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged. Water deeply and allow the top few inches of soil to dry out between waterings.
Q: Can I grow a Japanese Maple tree in a container?
A: Yes, Japanese Maples are well-suited for container gardening. Choose a large pot with adequate drainage holes and use a well-draining potting mix. Ensure the container is placed in a partially shaded location.
Q: How do I prune a Japanese Maple?
A: Pruning Japanese Maples is necessary to maintain their desired shape and remove any dead or diseased branches. Prune during late winter or early spring before new growth begins. Consult a pruning guide or seek professional help to ensure proper pruning techniques.
Q: Are Japanese Maples prone to any diseases or pests?
A: Japanese Maples can be susceptible to fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and verticillium wilt. Pests like aphids, scale insects, and caterpillars may also infest them. Regular inspections and appropriate treatment methods can help keep these issues in check.
Q: Can I propagate Japanese Maples?
A: Yes, Japanese Maples can be propagated through various methods such as seed germination, grafting, or taking stem cuttings. However, grafting is the most reliable way to reproduce a specific cultivar.
Q: How long does it take for a Japanese Maple tree to reach maturity?
A: Japanese Maples are relatively slow-growing trees. It can take several years, typically around 10-15 years, for a Japanese Maple to reach its full size and show its true beauty.
Q: Can Japanese Maples be used as bonsai trees?
A: Yes, Japanese Maples are popular choices for bonsai due to their elegant and delicate foliage. With proper care and training techniques, they can be grown as stunning bonsai specimens.
Planting & Care
Planting & Care for Japanese Maple (Acer Palmatum)
Planting:
- Choose a location with partial shade to protect the tree from harsh afternoon sun.
- Ensure the soil is well-draining and slightly acidic (pH between 5.5 and 6.5).
- Dig a hole that is twice as wide as the root ball and slightly shallower.
- Place the tree in the hole, making sure the root collar is level with or slightly above the soil surface.
- Backfill the hole with soil and gently firm it around the roots to eliminate air pockets.
- Water thoroughly after planting to settle the soil.
Watering:
- Japanese maples require regular watering, especially during dry periods.
- Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Water at the base of the tree, avoiding wetting the foliage as it can promote disease.
- Apply a layer of organic mulch around the tree to help retain moisture.
Fertilizing:
- Japanese maples benefit from an annual application of balanced fertilizer in early spring before new growth starts.
- Use a slow-release fertilizer specifically formulated for acid-loving plants.
- Follow the packaging instructions for proper application rates.
- Avoid applying fertilizer too close to the trunk to prevent root burn.
Pruning:
- Prune Japanese maples in late winter or early spring when the tree is dormant.
- Remove any dead or damaged branches using clean, sharp pruning shears.
- Thin out overcrowded areas to improve air circulation and light penetration.
- Shape the tree according to your desired form by selectively pruning branches.
Pest & Disease Control:
- Regularly inspect the tree for signs of pests such as aphids, scale insects, or mites.
- If pests are present, use an appropriate insecticidal soap or horticultural oil to control them.
- Prevent fungal diseases by avoiding overhead watering and ensuring adequate air circulation.
- If leaf spot or powdery mildew occurs, apply a fungicide according to the label instructions.
Winter Care:
- Japanese maples are generally hardy, but young trees may benefit from winter protection.
- Apply a layer of mulch around the base of the tree to insulate the roots.
- Consider wrapping the tree with burlap if severe cold or strong winds are expected.
- Avoid using plastic wraps as they can trap moisture and promote disease.
Item has been added to your cart.